Meditation Practice Does Not Change the Brain or Impulsivity
By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
“Impulsivity is a characteristic of human behavior that can be both beneficial and detrimental to our everyday lives. For example, the ability to act on impulse may allow us to seize a valuable opportunity, or to make a disastrous decision that we then live to regret.” – Catharine Winstanley
Impulsivity “is a tendency to act on a whim, displaying behavior characterized by little or no forethought, reflection, or consideration of the consequences.” It can lead to taking unnecessary risks with at times disastrous consequences. It can also lead to inappropriate aggressive behavior also potentially leading to disastrous consequences including disciplinary problems and even criminal prosecution. There are some indications that mindfulness can help to reduce impulsivity. But there is a need for more study of this potential benefit of mindfulness.
The nervous system is a dynamic entity, constantly changing and adapting to the environment. It will change size, activity, and connectivity in response to experience. These changes in the brain are called neuroplasticity. Over the last decade neuroscience has been studying the effects of contemplative practices on the brain and has identified neuroplastic changes in widespread areas. In other words, meditation practice appears to mold and change the brain, producing psychological, physical, and spiritual benefits. The types of neural changes produced by meditation practice that might underlie changes in impulsivity have not been investigated.
In today’s Research News article “The Effect of Mindfulness Meditation on Impulsivity and its Neurobiological Correlates in Healthy Adults.” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6700173/), Korponay and colleagues recruited long-term meditators with at least 3 years of experience and meditation naïve adults. They were measured for mindfulness, impulsivity and behavioral inhibition with a go-no-go task. In addition, their brains were scanned with functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) and their spontaneous eye blinks recorded. Then the meditation naïve participants were randomly assigned to receive either an 8-week Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) program, an 8-week health education program, or a wait-list control condition. After treatment they underwent the same measurements.
They found that after the interventions the Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) group had significantly higher levels of mindfulness but there were no significant changes in impulsivity or behavioral inhibition and no significant differences in brain volumes or connectivity, or in eye blink rates. Hence, short-term mindfulness training did improve mindfulness but did not produce changes in the brain or in impulsivity.
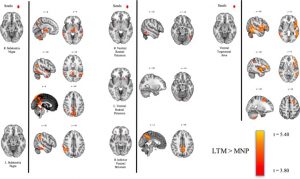
In comparing long-term meditators to meditation naïve participants, they found that the long-term meditators had lower attentional impulsivity, suggesting better attentional control, but higher motor and non-planning impulsivity. The long-term meditators had less striatal gray matter, greater cortico-striatal-thalamic functional connectivity, and lower spontaneous eye-blink rates.
The null findings regarding brain structural changes following Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) training are curious as prior research has consistently demonstrated that this training produces significant changes in the brain. Only in comparing long-term meditators to meditation naïve participants were significant differences detected. This suggests that the brain difference may have been not been due to the effects of the meditation itself, but rather to brain differences in people who are drawn to long-term meditation practice compared to people who are not drawn.
The present results suggest that neither long-term or short-term mindfulness practice changes impulsivity. Previous research found that mindfulness training reduced impulsivity in individuals who had difficulties with impulse control, prisoners, patients with borderline personality disorder, and out-of-control teenagers. It would appear that mindfulness training is effective in reducing impulsivity in people with low levels of impulse control but not in normal populations. Hence, mindfulness training is helpful for improving impulse control only where it is low to begin with.
“It seems the longer you do meditation, the better your brain will be at self-regulation. You don’t have to consume as much energy at rest and you can more easily get yourself into a more relaxed state.” – Bin He
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are also available on Google+ https://plus.google.com/106784388191201299496/posts and on Twitter @MindfulResearch
Study Summary
Korponay, C., Dentico, D., Kral, T., Ly, M., Kruis, A., Davis, K., … Davidson, R. J. (2019). The Effect of Mindfulness Meditation on Impulsivity and its Neurobiological Correlates in Healthy Adults. Scientific reports, 9(1), 11963. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-47662-y
Abstract
Interest has grown in using mindfulness meditation to treat conditions featuring excessive impulsivity. However, while prior studies find that mindfulness practice can improve attention, it remains unclear whether it improves other cognitive faculties whose deficiency can contribute to impulsivity. Here, an eight-week mindfulness intervention did not reduce impulsivity on the go/no-go task or Barratt Impulsiveness Scale (BIS-11), nor produce changes in neural correlates of impulsivity (i.e. frontostriatal gray matter, functional connectivity, and dopamine levels) compared to active or wait-list control groups. Separately, long-term meditators (LTMs) did not perform differently than meditation-naïve participants (MNPs) on the go/no-go task. However, LTMs self-reported lower attentional impulsivity, but higher motor and non-planning impulsivity on the BIS-11 than MNPs. LTMs had less striatal gray matter, greater cortico-striatal-thalamic functional connectivity, and lower spontaneous eye-blink rate (a physiological dopamine indicator) than MNPs. LTM total lifetime practice hours (TLPH) did not significantly relate to impulsivity or neurobiological metrics. Findings suggest that neither short- nor long-term mindfulness practice may be effective for redressing impulsive behavior derived from inhibitory motor control or planning capacity deficits in healthy adults. Given the absence of TLPH relationships to impulsivity or neurobiological metrics, differences between LTMs and MNPs may be attributable to pre-existing differences.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6700173/