Improve Type 2 Diabetes in the Elderly with Tai Chi
By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
“I have high blood sugars, and Type 2 diabetes is not going to kill me. But I just have to eat right, and exercise, and lose weight, and watch what I eat, and I will be fine for the rest of my life.” ― Tom Hanks
Diabetes is a major health issue. It is estimated that 30 million people in the United States have diabetes and the numbers are growing. Type 2 Diabetes results from a resistance of tissues, especially fat tissues, to the ability of insulin to promote the uptake of glucose from the blood. As a result, blood sugar levels rise producing hyperglycemia. Diabetes is the 7th leading cause of death in the United States. In addition, diabetes is heavily associated with other diseases such as cardiovascular disease, heart attacks, stroke, blindness, kidney disease, and circulatory problems leading to amputations. As a result, diabetes doubles the risk of death of any cause compared to individuals of the same age without diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes is largely preventable. One of the reasons for the increasing incidence of Type 2 Diabetes is its association with overweight and obesity which is becoming epidemic in the industrialized world. A leading cause of this is a sedentary lifestyle. Current treatments for Type 2 Diabetes focus on diet, exercise, and weight control. Recently, mindfulness practices have been shown to be helpful in managing diabetes. Tai Chi is mindfulness practice and a gentle exercise that has been found to improve the symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes. The research is accumulating. So, it is reasonable to examine what has been learned.
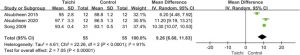
In today’s Research News article “Tai Chi Program to Improve Glucose Control and Quality of Life for the Elderly With Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-analysis.” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9111975/ ) Wang and colleagues review, summarize, and perform a meta-analysis of the published randomized controlled trials of the effectiveness of Tai Chi practice in the treatment of Type 2 Diabetes in elderly patients. They identified 7 published studies.
They report that after Tai Chi there were significant decreases in blood glucose levels and significant increases in balance and ability to perform independent life activities. Hence, in elderly Type 2 Diabetes patients Tai Chi practice results in better glucose control, improved ability to conduct their everyday lives and a reduced likelihood of falls.
“People take ownership of sickness and disease by saying things like MY high blood pressure MY diabetes, MY heart disease, MY depression, MY! MY! MY! Don’t own it because it doesn’t belong to you!” ― Stella Payton
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are also available on Twitter @MindfulResearch
Study Summary
Wang Y, Yan J, Zhang P, Yang P, Zhang W, Lu M. Tai Chi Program to Improve Glucose Control and Quality of Life for the Elderly With Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-analysis. Inquiry. 2022 Jan-Dec;59:469580211067934. doi: 10.1177/00469580211067934. PMID: 35282699; PMCID: PMC9111975.
Abstract
Objective
To systematically evaluate the effects of Tai chi for improving elderly patients with type 2 diabetes.
Methods
According to PRISMA checklist, we conducted this standard meta-analysis. The multiple databases like Pubmed, Embase, and Cochrane databases were used to search for the relevant studies, and full-text articles involved in the evaluation of Tai chi in improving elderly patients with type 2 diabetes. Review manager 5.2 was adopted to estimate the effects of the results among selected articles. Forest plots, sensitivity analysis and funnel plot for the articles included were also conducted.
Results
Finally, 7 relevant studies were eventually satisfied the included criteria. We found that Tai chi group had lower glucose than control group (mean difference (MD)=-12.47, 95%CI [-21.20, −3.73], P=.005; I 2 = 32%), Tai chi group had higher activities-specific balance confidence (ABC) scale than control group (MD =9.26 with 95%CI [6.68, 11.83], P < .001) and Tai chi group had higher single limb standing test score than control group (MD = 8.38, 95%CI [4.02, 12.74], P = .001). The study was robust and limited publication bias was observed in this study.
Conclusion
Since we found Tai chi had better performance than usual care in improving old diabetes patients’ glucose and life quality, the study supports that Tai chi can help old diabetes patients from several aspects including disease indicators, independence and life quality.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9111975/