By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
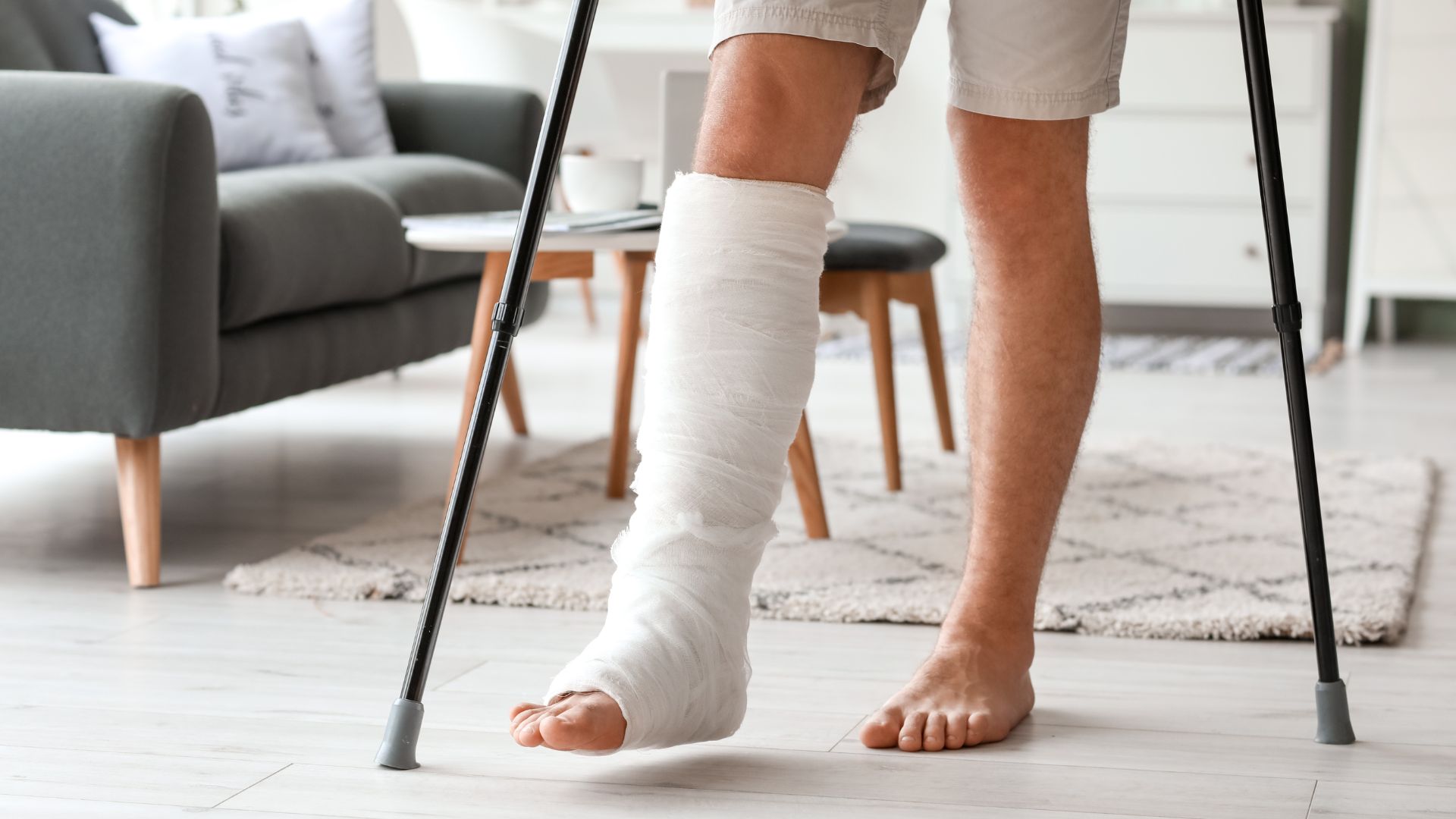
In today’s Research News article “The Role of Mindfulness Decompression Therapy in Managing Acute Stress Disorder in Traumatic Fracture Patients” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11726210/ ) Chen and colleagues examined the effectiveness of Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) therapy in alleviating the acute stress responses following traumatic bone fractures. These stress responses include traumatic experiences, persistent tension, irritability, and sleep disorders. They found that MBSR produced significant reductions in these acute stress response symptoms.
Treatment with Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) alleviates the acute stress response as a result of traumatic bone fractures.
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are also available on the Contemplative Studies Blog http://contemplative-studies.org
Study Summary
Chen X, Tian C, Zhang Y, Fu Y, Han W, Zhang R. The Role of Mindfulness Decompression Therapy in Managing Acute Stress Disorder in Traumatic Fracture Patients. Actas Esp Psiquiatr. 2025 Jan;53(1):71-79. doi: 10.62641/aep.v53i1.1668. PMID: 39801417; PMCID: PMC11726210.
Abstract
Background:
Traumatic fractures are common orthopedic injuries with higher incidence globally, leading to acute stress disorder (ASD). Therefore, this study aimed to analyze the clinical outcomes of mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) therapy in patients with traumatic bone fractures suffering from ASD.
Methods:
This study included 135 patients who underwent trauma and fracture treatment at The 305th Hospital of the PLA between August 2021 and August 2023. Based on their participation in MBSR therapy, they were categorized into a conventional group (n = 62) and a combined group (n = 73). We comparatively analyzed the ASD Scale (ASDS), Self-Rating Anxiety Scale (SAS), Self-Rating Depression Scale (SDS), Self-Rating Sleep Status Scale (SRSS), and World Health Organization Quality of Life (WHOQOL) measurement–BREF (WHOQOL–BREF) scores between these two experimental groups. Furthermore, we assessed the incidence of ASD after treatment between these two groups.
Results:
There were no significant differences in gender, age, body mass index, education, income, type of expense, trauma type, marital status, fracture site, diabetes status, hypertension status, and the pain visual analog scale (VAS) score, activities of daily living (i.e., modified Barthel index) score, and Social Support Rating Scale score between the two experimental groups (p > 0.05). Moreover, no significant differences were found in the prevalence of ASDS before treatment between these two groups (p > 0.05). However, after treatment, the ASDS score was significantly lower in the combined group than in the conventional group (p < 0.05). Furthermore, post-management analysis revealed that the incidence rate of ASD was 24.19% in the conventional group and 8.22% in the combined group. Moreover, the incidence of ASD was significantly lower in the combined group compared to the conventional group (p < 0.05). Before intervention, the difference in the SAS or SDS between patients was not statistically significant (p > 0.05). However, following treatment, the SAS and SDS scores of patients were significantly lower in the combined group than in the conventional group (p < 0.05). Similarly, after treatment, the SRSS scores of patients were substantially lower in the combined group than in the conventional group (p < 0.05). Furthermore, the WHOQOL–BREF score of patients was significantly greater in the combined group than in the conventional group (p < 0.05).
Conclusion:
MBSR therapy can significantly alleviate ASD in trauma and fracture patients. Furthermore, this approach can alleviate the incidence of ASD and reduce anxiety, depression, and negative emotions in patients. These positive effects collectively improve sleep quality and overall well-being of patients.