Reduce Depression in Older Adults with Mind-Body Practices and Exercise
By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
“Complementary use of mindful exercise, such as Tai Chi and yogic meditation, can improve clinical outcomes of mood disorders in older adults-as demonstrated in brain scans, biomarkers of cellular aging, and mental health rating scales.” – Arline Kaplan
The aging process involves a systematic progressive decline in every system in the body, the brain included. This includes our cognitive (mental) abilities and mood. It is inevitable and cannot be avoided. There is some hope for age related decline, however, as there is evidence that it can be slowed. There are some indications that physical and mental exercise can reduce the rate of decline. For example, contemplative practices such as meditation, yoga, and Tai Chi or qigong have all been shown to be beneficial in slowing or delaying physical and mental decline with aging and with improving depression. The research has been accumulating. So, it makes sense to pause and review and summarize what has been learned.
In today’s Research News article “Aerobic, resistance, and mind-body exercise are equivalent to mitigate symptoms of depression in older adults: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8191520/ ) Miller and colleagues review, summarize, and perform a meta-analysis of the published randomized controlled trials of the effectiveness of mind-body practices, aerobic exercise, and resistance exercise on depression in older adults (over 65 years of age). They identified 69 published research studies including a total of 5,379 elderly participants.
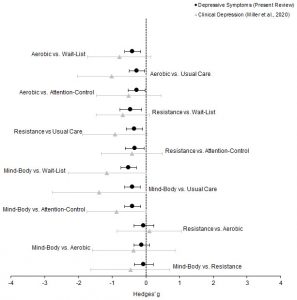
They report that the published research found that in comparison to usual care, wait-list controls, or attention controls that mind-body practices, aerobic exercise, and resistance exercise all significantly reduced depression in the elderly participants. Although no significant differences were found between the practices, on average, the effectiveness of the practices were rank ordered mind-body practices followed by aerobic exercise followed by resistance exercise.
All three practices involve exercise. Mind-body practices include yoga, Tai Chi, and Qigong all of which provide gentle mild exercise intensity. Aerobic exercise on the other hand provides moderate intensity exercise. This suggests that the intensity of exercise is not important for the relief of depression. What does appear to be important is that exercise be incorporated into the activities of the elderly to raise mood and reduce depression. Hence, the results suggest that the depression that is common in the elderly can be ameliorated with exercise.
So, reduce depression in older adults with mind-body practices and exercise.
“Higher physical activity levels among older adults in particular may have a preventive effect on the development of depression.36 Recent findings point to the potential efficacy of exercise as a treatment of depression in older adults, in some cases with similar efficacy to antidepressants.” – Maren Nyer
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are also available on Google+ https://plus.google.com/106784388191201299496/posts and on Twitter @MindfulResearch
Study Summary
Miller, K. J., Areerob, P., Hennessy, D., Gonçalves-Bradley, D. C., Mesagno, C., & Grace, F. (2020). Aerobic, resistance, and mind-body exercise are equivalent to mitigate symptoms of depression in older adults: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. F1000Research, 9, 1325. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.27123.2
Abstract
Background: Exercise has been identified as an allied health strategy that can support the management of depression in older adults, yet the relative effectiveness for different exercise modalities is unknown. To meet this gap in knowledge, we present a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials (RCTs) to examine the head-to-head effectiveness of aerobic, resistance, and mind-body exercise to mitigate depressive symptoms in adults aged ≥ 65 years.
Methods: A PRISMA-NMA compliant review was undertaken on RCTs from inception to September 12 th, 2019. PubMed, Web of Science, CINAHL, Health Source: Nursing/Academic Edition, PsycARTICLES, PsycINFO, and SPORTDiscus were systematically searched for eligible RCTs enrolling adults with a mean age ≥ 65 years, comparing one or more exercise intervention arms, and which used valid measures of depressive symptomology. Comparative effectiveness was evaluated using network meta-analysis to combine direct and indirect evidence, controlling for inherent variation in trial control groups.
Results: The systematic review included 82 RCTs, with 69 meeting eligibility for the network meta-analysis ( n = 5,379 participants). Pooled analysis found each exercise type to be effective compared with controls (Hedges’ g = -0.27 to -0.51). Relative head-to-head comparisons were statistically comparable between exercise types: resistance versus aerobic (Hedges’ g = -0.06, PrI = -0.91, 0.79), mind-body versus aerobic (Hedges’ g = -0.12, PrI = -0.95, 0.72), mind-body versus resistance (Hedges’ g = -0.06, PrI = -0.90, 0.79). High levels of compliance were demonstrated for each exercise treatment.
Conclusions: Aerobic, resistance, and mind-body exercise demonstrate equivalence to mitigate symptoms of depression in older adults aged ≥ 65 years, with comparably encouraging levels of compliance to exercise treatment. These findings coalesce with previous findings in clinically depressed older adults to encourage personal preference when prescribing exercise for depressive symptoms in older adults.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8191520/