Reduce Biochemical Stress Responses in Hispanic Breast Cancer Patients with Mindfulness
By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
“Mindfulness is a state of mind which we can all acquire and use to support our wellbeing physically, emotionally and mentally. . . Having cancer, or specifically breast cancer. . . experiences take up a lot of energies, mental focus and can drain us emotionally. It is important to have a few tools to help us create ‘down’ and ‘out’ times, and to replenish and reconnect with who we are.“ – Karin Sieger
Because of great advances in treatment, many patients today are surviving cancer. But cancer survivors frequently suffer from anxiety, depression, mood disturbance, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), sleep disturbance, fatigue, sexual dysfunction, loss of personal control, impaired quality of life, and psychiatric symptoms which have been found to persist even ten years after remission. Also, cancer survivors can have to deal with a heightened fear of reoccurrence. This is particularly true with metastatic cancer. So, safe and effective treatments for the symptoms in cancer and the physical and psychological effects of the treatments are needed.
Mindfulness training has been shown to help with general cancer recovery . Mindfulness practice have been shown to improve the residual symptoms in cancer survivors. Most research, however, examines women from affluent western populations and may not be sensitive to the unique situations, cultures, and education levels of diverse populations. There are indications that mindfulness therapies may be effective in diverse populations. But there is a need for further investigation with different populations.
In today’s Research News article “). A Large Randomized Trial: Effects of Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) for Breast Cancer (BC) Survivors on Salivary Cortisol and IL-6.” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6700883/), Lengacher and colleagues recruited adult breast cancer survivors and randomly assigned them to receive either usual care of a once a week for 2 hours, 6 week program of Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) modified for breast cancer patients. The program included meditation, body scan, yoga practices, and discussion along with daily home practice. At baseline, before and after the MBSR session at weeks 1 1nd 6, and after treatment the participants provided saliva samples that were assayed for cortisol and IL-6 levels. They also completed questionnaires measuring fear of cancer recurrence, depression, anxiety, perceived stress, sleep, fatigue, and quality of life.
They found that in comparison to baseline and the usual care group, the group that received Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) had significant reductions in both cortisol and IL-6 levels. In addition, both cortisol and IL-6 levels decreased significantly over the course of the MBSR sessions at weeks 1 1nd 6. They also found that the higher the levels of IL-6 at baseline and the end of treatment the higher the levels of fear of cancer recurrence, sleep problems and fatigue and the lower the levels of quality of life and physical health. After MBSR they found that the higher the levels of IL-6 the higher the levels of fear of cancer recurrence, depression, pain, perceived stress, sleep disturbance and fatigue and the lower the levels of quality of life and physical health.
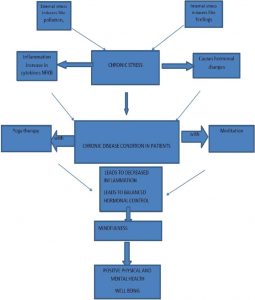
Cortisol and IL-6 levels are markers of stress and inflammation. So, these results suggest that Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) reduces the biochemical markers of stress and inflammation in breast cancer survivors and that the levels of IL-6, an inflammatory cytokine, are related to their health and well-being. These findings lend support to prior findings that mindfulness training is an effective treatment for the psychological health of breast cancer survivors and demonstrate that this may, at least in part, be due to the effects of mindfulness training on stress hormones and inflammatory biomarkers. The ability of mindfulness training to reduce stress and inflammatory responses is thought to be a primary mechanism by which it improves health and well-being.
The results also demonstrate that Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) treatment is effective in Hispanic breast cancer survivors. This suggests that MBSR is an effective treatment across ethnic groups. MBSR appears to effectively reduce stress and inflammatory responses regardless of ethnicity and produce improvements in health and well-being.
So, reduce biochemical stress responses in Hispanic breast cancer patients with mindfulness.
“Mindfulness is a good resource for dealing with the physical and psychological symptoms of metastatic disease. Women who were more mindful tended to have lower symptoms of metastatic breast cancer, including pain severity and interference, fatigue, psychological distress, and sleep disturbance.” – Lauren Zimmaro
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are also available on Google+ https://plus.google.com/106784388191201299496/posts and on Twitter @MindfulResearch
Study Summary
Lengacher, C. A., Reich, R. R., Paterson, C. L., Shelton, M., Shivers, S., Ramesar, S., Pleasant, M. L., Budhrani-Shani, P., Groer, M., Post-White, J., Johnson-Mallard, V., Kane, B., Cousin, L., Moscoso, M. S., Romershausen, T. A., & Park, J. Y. (2019). A Large Randomized Trial: Effects of Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) for Breast Cancer (BC) Survivors on Salivary Cortisol and IL-6. Biological research for nursing, 21(1), 39–49. https://doi.org/10.1177/1099800418789777
Abstract
Breast cancer survivors (BCS) often experience psychological and physiological symptoms after cancer treatment. Mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR), a complementary and alternative therapy, has reduced subjective measures of stress, anxiety, and fatigue among BCS. Little is known, however, about how MBSR affects objective markers of stress, specifically the stress hormone cortisol and the pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6). In the present study, BCS (N = 322) were randomly assigned to a 6-week MBSR program for BC or usual-care control. Measurements of cortisol, IL-6, symptoms, and quality of life were obtained at orientation and 6 weeks. Cortisol and IL-6 were also measured prior to and after the MBSR(BC) class Weeks 1 and 6. The mean age of participants was 56.6 years and 69.4% were White non-Hispanic. Most had Stage I (33.8%) or II (35.7%) BC, and 35.7% had received chemotherapy and radiation. Cortisol levels were reduced immediately following MBSR(BC) class compared to before the class Weeks 1 and 6 (Wilcoxon-signed rank test; p < .01, d = .52–.56). IL-6 was significantly reduced from pre- to postclass at Week 6 (Wilcoxon-signed rank test; p < .01, d = .21). No differences were observed between the MBSR(BC) and control groups from baseline to Week 6 using linear mixed models. Significant relationships with small effect sizes were observed between IL-6 and both symptoms and quality of life in both groups. Results support the use of MBSR(BC) to reduce salivary cortisol and IL-6 levels in the short term in BCS.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6700883/