By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
In today’s Research News article “Effects of Tai Chi and Qigong intervention on anxiety and stress in diabetic and hypertensive Brazilian patients: a randomized controlled trial” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC12002851/ ) Santos and colleagues examined the effects of a 13 week Tai Chi and Qigong intervention on the psychological health of patients with diabetes or hypertension. They found that Tai Chi and Qigong significantly reduced the levels of anxiety and stress in these patients.
Reduce anxiety and stress in patients with diabetes or hypertension with Tai Chi and Qigong.
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are also available on the Contemplative Studies Blog http://contemplative-studies.org
Study Summary
Santos LRAC, Taíra A, Possobon RF, Meneghim MC, Su CL, Lavin P, Rej S, Ambrosano GMB, Cortellazzi KL. Effects of Tai Chi and Qigong intervention on anxiety and stress in diabetic and hypertensive Brazilian patients: a randomized controlled trial. Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2025 Mar 24;23:eAO1076. doi: 10.31744/einstein_journal/2025AO1076. PMID: 40353827; PMCID: PMC12002851.
In Brief
A 13-week Tai Chi/Qigong intervention reduced anxiety and stress in middle-aged and older Brazilian patients with diabetes and hypertension. With significant improvements in the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory and PSS14 scores, this practice shows potential as an effective adjunctive therapy in primary care.
ABSTRACT
Objective:
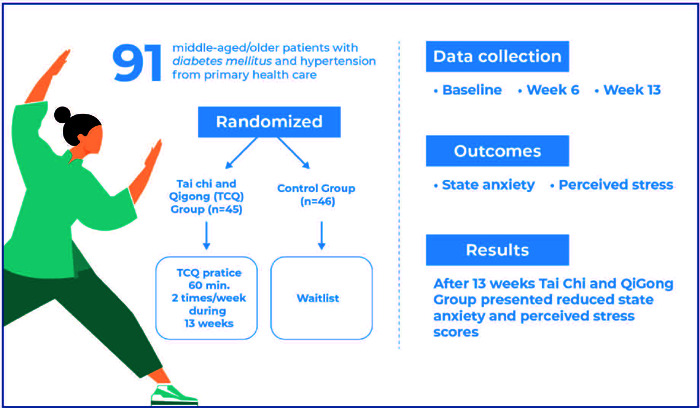
This study investigated the effects of Tai Chi/Qigong practice over 13 weeks on anxiety and perceived stress levels in middle-aged or older Brazilian hypertensive and diabetic individuals assisted in a primary healthcare setting.
Methods:
Ninety-one patients with diabetes mellitus and/or hypertension diagnosed and followed up at a primary care center were randomized to the Tai Chi/Qigong intervention (n = 45) or waitlist (n = 46) group for 13 weeks. Outcome measures were collected at baseline and at 6 and 13 weeks for anxiety (State-Trait Anxiety Inventory [STAI]) and stress (Perceived Stress Scale – PSS14). The primary endpoint of the study was 13 weeks. We used a linear mixed-effects model to analyze the primary and secondary outcomes, considering the treatment group and time as covariates and treating the subject as a random effect.
Results:
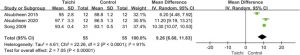
Of the included 91 participants, 53 completed the 6-week assessment, and 42 completed the 13-week assessment. After 13 weeks, the Tai Chi/Qigong Group had lower scores for anxiety (STAI Estimate = -6.421; SD = 2.679; 95% confidence interval (95%CI) = [-11.615,-1.224]; p = 0.018) and stress (PSS14 Estimate = -9.290; SD= 2.262; 95%CI= [-13.678,-4.906]; p<0.001).
Conclusion:
A 13-week Tai Chi/Qigong intervention was efficacious in lowering anxiety and perceived stress scores in middle-aged and older patients with diabetes mellitus and hypertension and can potentially be used in primary care centers as an adjunct therapy.
Highlights
A 13-week Tai Chi/Qigong program significantly reduced anxiety and stress in Brazilian patients with diabetes and hypertension.
Tai Chi/Qigong offers an effective complementary therapy to improve health outcomes in primary care settings.
This study highlights the potential of Tai Chi/Qigong for enhancing mental and physical well-being in chronic disease management.