Mindfulness Increases Self-Forgiveness in Prisoners
By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
“We must develop and maintain the capacity to forgive. He who is devoid of the power to forgive is devoid of the power to love,” – Martin Luther King Jr.
Around 2 ¼ million people are incarcerated in the United States. Even though prisons are euphemistically labelled correctional facilities very little correction actually occurs. This is supported by the rates of recidivism. About three quarters of prisoners who are released commit crimes and are sent back to prison within 5-years. The lack of actual treatment for the prisoners leaves them ill equipped to engage positively in society either inside or outside of prison. Hence, there is a need for effective treatment programs that help the prisoners while in prison and prepares them for life outside the prison.
Forgiveness is important to happiness and psychological well-being. It allows one to move beyond anger and resentment. It is an adaptive ability to move beyond a perceived transgression by another, not by ignoring or denying it, but by reframing it so the response moves away from negativity. This is true not only of others but also the self. Self-forgiveness is essential for psychological well-being. This may be particularly important for prisoners. There is emerging research on forgiveness but much has yet to be explored regarding the processes that lead to and improve forgiveness. Mindfulness has been found to be associated with higher levels of forgiveness. So, it makes sense to explore the processes by which mindfulness is associated with forgiveness in prisoners.
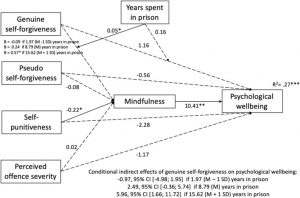
In today’s Research News article “The relationship between self-forgiveness and psychological wellbeing in prison inmates: The mediating role of mindfulness.” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9826273/ ) Paleari and colleagues recruited male prisoners and had them complete measures of years in prison, mindfulness, self-forgiveness for the crime committed, well-being, and severity of the crime committed.
They found that self-forgiveness had an indirect effect on well-being in the prisoners mediated by mindfulness such that self-forgiveness was positively associated with mindfulness which was in turn positively associated with well-being. This was particularly true for prisoners who had spent years in prison.
So, the ability of self-forgiveness to improve the psychological well-being of prisoners was mediated by mindfulness. Perhaps mindfulness training might amplify this effect.
“It’s not an easy journey, to get to a place where you forgive people. But it is such a powerful place, because it frees you.” – Tyler Perry
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are also available on Twitter @MindfulResearch
Study Summary
Paleari GF, Danioni F, Pelucchi S, Lombrano MR, Lumera D, Regalia C. The relationship between self-forgiveness and psychological wellbeing in prison inmates: The mediating role of mindfulness. Crim Behav Ment Health. 2022 Oct;32(5):337-349. doi: 10.1002/cbm.2260. Epub 2022 Sep 2. PMID: 36056526; PMCID: PMC9826273.
Abstract
Background
Previous research with general population samples has consistently shown that forgiveness and mindfulness facilitate coping with distressing experiences and significantly promote mental health. No study, however, has examined their unique contribution to prisoners’ psychological wellbeing nor has considered the different forms of self‐forgiveness among prisoners.
Aims
Our aim was to investigate the role of mindfulness in mediating any association between prisoners’ self‐forgiveness and psychological wellbeing and to test whether any such links are moderated by years spent in prison. In this study self‐forgiveness was conceptualised as a multidimensional construct, including presence of genuine self‐forgiveness, absence of pseudo self‐forgiveness and/or absence of self‐punitiveness.
Methods
Participants were recruited from a prison in Northern Italy. Consenting men were asked to complete an anonymous self‐report questionnaire with only a researcher present.
Results
104 male prisoners (mean age 46.63 years, SD 11.38) took part. Findings were that self‐punitiveness was inversely related to well‐being, with mindfulness mediating this relationship, this while controlling for the other dimensions of self‐forgiveness and the perceived severity of the crime committed. Contrary to expectation, we found no direct relationship between genuine self‐forgiveness and well‐being, but the moderated mediation models showed that genuine self‐forgiveness was positively associated with mindfulness and, through this, had an indirect association with wellbeing, significant only for prisoners who had already spent several years in prison.
Conclusions
Our findings confirm that self‐forgiveness is a complex construct, worthy of further investigation among offenders. They suggest that forgiveness interventions for prisoners should include modules aimed at primarily reducing self‐punitive attitudes. Promotion of genuine self‐forgiveness should be tried only with awareness that this is likely to take a very long time. In such circumstances, interventions may promote energy to be invested in mindful processes with a consequent improvement in psychological wellbeing.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9826273/