By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
In today’s Research News article “How does meditation relate to quality of life, positive lifestyle habits and carbon footprint?” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11730546/) Somarathne and colleagues examined the environmentally friendly behaviors of skilled meditators. They found that meditator’s mindfulness was associated with higher levels of environmentally friendly behaviors.
Hence, mindfulness is associated with environmentally friendly behaviors.
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are also available on the Contemplative Studies Blog http://contemplative-studies.org
Study Summary
Somarathne EASK, Gunathunga MW, Lokupitiya E. How does meditation relate to quality of life, positive lifestyle habits and carbon footprint? Heliyon. 2024 Dec 12;11(1):e41144. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e41144. PMID: 39811348; PMCID: PMC11730546.
Abstract
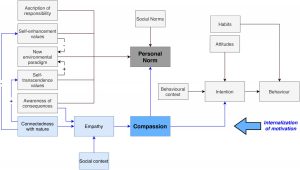
There is increasing scientific interest in the potential links between meditation practice and pro-environmental behaviours. The present research investigates relationships between Vipassana meditation experience (temporal variables of meditation, five facets of trait mindfulness), positive lifestyle habits (PLH), quality of life (QoL) and per-head carbon footprint (CF) among 25 skilled meditators. Self-reported validated questionnaires were given to a group of native speakers of Sri Lanka to collect data on meditation experience, PLH, and perceived QoL. In estimating CF four domains (food and beverage consumption, electricity consumption, traveling and solid waste disposal) were considered. Correlation analyses revealed that trait mindfulness showed strong associations (r > 0.4) with PLH. None of the temporal variables of meditation experience was significantly correlated with any domain of CF. Two facets of mindfulness (observing and non-reactivity to present-moment experience) demonstrated statistically strong associations (p < 0.05) with perceived QoL. It was found that the PLH significantly mediates the relationship between the observing facet of trait mindfulness and CF associated with food and beverage consumption (indirect effect – 0.002, SE = 0.001 95 % CI [0.010, 0.417]). Further, the relationship between acting with awareness and CF associated with solid waste disposal at landfill sites was significantly mediated by the PLH (indirect effect – (−0.003), SE = 0.003 95 % CI [-0.012, −0.0001]). The current study will serve as a foundation for future longitudinal studies on the same subject by providing evidence for the relationships between meditation experience and PLH, perceived QoL and CF
Environment
Improve Positive Psychological States with Mindfulness
Improve Positive Psychological States with Mindfulness
By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
“So how does meditation lead to greater happiness? “Loving-kindness is designed to elicit positive emotions. We are stretching the way we pay attention by looking for the good in ourselves or wishing ourselves well through loving-kindness.” – Caren Osten
“Meditation leads to concentration, concentration leads to understanding, and understanding leads to happiness” – This wonderful quote from the modern-day sage Thich Nhat Hahn is a beautiful pithy description of the benefits of mindfulness practice. Mindfulness allows us to view our experience and not judge it, not put labels on it, not make assumptions about it, not relate it to past experiences, and not project it into the future. Rather mindfulness lets us experience everything around and within us exactly as it is arising and falling away from moment to moment. Mindfulness meditation has been shown to increase positive emotions and happiness. But there is a need to further investigate the effects of mindfulness on positive emotional states.
In today’s Research News article “A New Second-Generation Mindfulness-Based Intervention Focusing on Well-Being: A Randomized Control Trial of Mindfulness-Based Positive Psychology.” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8976107/ ) Zheng and colleagues recruited healthy adults and randomly assigned them to either a wait-list control condition or to receive mindfulness meditation instruction for 2.5 hours per week for 6 weeks followed by 20 minutes of meditation practice along with home practice. They were measured before, during (every 2 weeks), after, and 3 months after the treatment for satisfaction with life, positive and negative emotions, psychological well-being, mindfulness, attitudes toward self and others, and self-compassion.
They found that the mindfulness meditation program produced a significant reduction in negative emotions and significant increases in self-compassion and environmental mastery. They also found that the greater the amount of meditation practice the higher the levels of positive emotions, positive relations, and awareness.
So, mindfulness meditation increased positive psychological states in healthy adults.
“In order to have the resiliency to face difficulties . . . we need to find and nurture the positive parts of ourselves, and make a point of paying attention to experiences that give us pleasure.” – Sharon Salzberg
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are also available on Twitter @MindfulResearch
Study Summary
Zheng, Y., Zhou, J., Zeng, X., Jiang, M., & Oei, T. (2022). A New Second-Generation Mindfulness-Based Intervention Focusing on Well-Being: A Randomized Control Trial of Mindfulness-Based Positive Psychology. Journal of happiness studies, 1–22. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-022-00525-2
Abstract
Second-generation mindfulness-based interventions (SG-MBIs) align well with positive psychology philosophy and practices, but trials of SG-MBIs have largely focused on ill-being. This study developed a mindfulness-based positive psychology (MBPP) intervention integrating positive psychology with an SG-MBI to enhance well-being. A randomized control trial was performed to compare MBPP with a waitlist condition among 138 Chinese participants. The results showed that MBPP significantly reduced negative emotions for subjective well-being and significantly improved environmental mastery for psychological well-being. Improvements in self-compassion and negative attitudes but not avoidance, mediated changes in well-being. Changes in positive emotions, positive relations, and awareness were associated with the amount of meditation practice. These findings showed that MBPP is promising for improving well-being and that the positive psychology components play important roles. Broadly, the study illustrated that positive psychology and SG-MBIs can be effectively integrated, and it supported the further application of SG-MBIs from the positive psychology perspective.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8976107/
Meditation Experience is Associated with Increased Concern for and Impact on the Environment
Meditation Experience is Associated with Increased Concern for and Impact on the Environment
By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
“Mindfulness . . . promotes environmental sustainability. It helps individuals disengage from automatic thoughts and become more open to behavioral change and freedom to make different choices. Examples of mindful behaviors include bringing a reusable bag to the grocery store, taking shorter showers, refilling personal water bottles instead of using a disposable bottle and using your purchasing power as a consumer to support companies with more sustainable practices.” – Menchi Liu
The ability of humans to manipulate and control the environment has developed to the point that human activity is now threatening to destroy that environment. This can be seen in the rapid extinction of once thriving species, the loss of forestation, the historic rise in atmospheric carbon dioxide levels, sea level rise, and climate change. It has been argued that we may have crossed a tipping point where the environmental damage is irreversible. But, if we haven’t, there is a pressing need to address the very activities that are producing the damage. We need to begin acting more responsibly toward our environment to reverse and heal the damage,
This will require actions by humans. This will require positive ecological behaviors. Ecological behavior is defined “as behaviors that protect/avoid harm to the environment and span all areas of life such as nutrition, mobility and transportation, energy and water consumption, waste avoidance, and consumerism.” In other words, humans need to change their behaviors toward more sustainable patterns.
Mindfulness promotes awareness of the internal and external environments. As such, it promotes sensitivity to these environments and to the impact of our actions on ourselves and the environment. In fact, mindfulness has been shown to be associated with the individual’s feelings of connectedness to nature. It is thus possible that mindfulness can stimulate ecological behavior and be a positive force for reversing the damage to our precious environment.
In today’s Research News article “Practice Matters: Pro-environmental Motivations and Diet-Related Impact Vary With Meditation Experience.” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.584353/full?utm_source=F-AAE&utm_medium=EMLF&utm_campaign=MRK_1757290_a0P58000000G0YfEAK_Psycho_20211021_arts_A ) Thiermann and colleagues recruited adult participants online who had varied diets and had them complete a questionnaire measuring their mindfulness practices, mindfulness, motivation, happiness, connection to the natural world, and animal protein consumption.
They separated the participants into 3 groups depending upon the amount of meditation they practiced, no practice, novice meditators, and advanced meditators. They found that the advanced meditations in comparison to the two other groups had significantly higher levels of mindfulness, happiness, connection to the natural world, integrated motivation, intention to reduce the intake of animal proteins, and concerns about the environment as a reason for reduced animal protein, and lower levels of introjected motivation. They also modelled the impact of each participants’ diets on greenhouse gas emissions, water use, and land use and found that the advanced meditators had significantly lower environmental impacts.
This study compared existing groups and as such causation cannot be determined as people who choose to meditate may be very different types of people than those who do not. Nevertheless, it is clear that meditators, particularly experienced meditators, have better psychological well-being, greater environmental consciousness, and lower impact on the environment. This does not establish meditation as a solution to the degradation of the environment. Future research needs to examine the effects of meditation training on environmentally impactful behaviors to determine if meditation can cause better ecological behaviors..
So, meditation experience is associated with increased concern for and impact on the environment.
“A sense of awareness, empathy, and connection with our surroundings, as well as an ability to create innovative solutions, are necessary and vital for solving any global issues facing our world today.” – Art of Living
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are also available on Google+ https://plus.google.com/106784388191201299496/posts and on Twitter @MindfulResearch
Study Summary
Thiermann UB, Sheate WR and Vercammen A (2020) Practice Matters: Pro-environmental Motivations and Diet-Related Impact Vary With Meditation Experience. Front. Psychol. 11:584353. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.584353
Mindfulness has emerged as a potential motivator for sustainable lifestyles, yet few studies provide insight into the relationship between mindfulness practice levels and individual engagement in pro-environmental behaviors. We also lack information about the significance of meditators’ behavioral differences in terms of their measurable environmental impact and the motivational processes underlying these differences in pro-environmental performance. We classified 300 individuals in three groups with varying meditation experience and compared their pro-environmental motivations and levels of animal protein consumption. Exceeding prior attempts to compare high-impact behaviors of mindfulness practitioners and non-practitioners, we created the most detailed classification of practice engagement by assessing frequency, experience and type of meditation practice. This nuanced view on mindfulness practice reveals that advanced meditators, who reported high levels of connectedness with nature (CWN), subjective happiness and dispositional mindfulness showed significantly more concern for the environment. They also demonstrated the lowest levels of greenhouse gas emissions, land occupation and water use related to their animal-protein consumption. This study is the first to follow a self-determination theory perspective to deepen our understanding of the motivational differences between meditator groups. We revealed that advanced meditators reported significantly more integrated motivation toward the environment than non-meditators. We also provided preliminary evidence for a new theoretical framework suggesting that experiential strategies such as mindfulness practices could strengthen the relational pathway of pro-environmental behaviors. Using sequential mediation analysis, we confirmed that the negative effect of mindful compassion practice on greenhouse gas emissions from animal-protein consumption is partially mediated by CWN and integrated motivation toward the environment. While our study does not support assumptions of causality, it shows that much can be learned by studying the motivations of advanced meditators for maintaining high levels of pro-environmental behavior.
“I am That” 2 – implications for everyday life.

In a previous post the well know phrase “I am that” originating with Nisargadatta Marajah was interpreted to indicate that there is no “I” or “that.” They are one. They are exactly the same thing as all other things. There is no distinction. Although this is a deep spiritual teaching, it also has implications for our everyday lives.
If indeed everything is the same and simply an expression of the whole inseparable reality then everything should treated with great reverence. We should have as much regard for garbage as we have for ourselves. In fact, a notable characteristic of Zen Masters is that they gladly engage is mundane and seemingly distasteful tasks such as cleaning floors and toilets with the same joy and reverence that they treat meditation. If everything is one then there is no distinction between good and bad things or between engaging and distasteful activities.
This also holds true for other people. If we are all one then there is no reason to act toward anyone any different from anyone else. The Great Commandment ‘Love your neighbor as yourself’ makes perfect sense as your neighbor is yourself.
Acting negatively or destructively toward anything or anyone degrades the whole which includes the self. It makes no sense to do so. It is in essence self-injurious to harm a flea. The environment deserves the same reverence as people as there is no distinction between the two. To cut down rain forests is equivalent to amputating a leg they are equally injurious to the singular one.
In most spiritual teachings love is a focus. We are told to love our neighbor and even our enemy. If they and us are one, of course we should love them all. To the sage, the oneness of all things is the essence of love. Everything is love. The first Great Commandment to ‘Love the Lord your God with all your heart and with all your soul and with all your mind’ also makes sense as everything is the Devine and everything is love.
So, the teaching of ‘I am that’ is the foundation upon which most spiritual teachings rest. I we truly accept that ‘I am that’ then we will live our lives very differently, with reverence, love, and respect for everything.