Mindfulness is a Cost-Effective Treatment to Prevent Depression Relapse
By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
“MBCT significantly reduces the rates of depressive relapse or recurrence compared with usual care or placebo, corresponding to a relative risk reduction of 34%.” – Willem Kuyken
Clinically diagnosed depression is the most common mental illness, affecting over 6% of the population. Major depression can be quite debilitating, impairing the ability of the patients to effectively conduct their lives. Depression can be difficult to treat and is usually treated with anti-depressive medication. But, of patients treated initially with drugs only about a third attained remission of the depression. After repeated and varied treatments including drugs, therapy, exercise etc. only about two thirds of patients attained remission. But drugs often have troubling side effects and can lose effectiveness over time. In addition, many patients who achieve remission have relapses and recurrences of the depression. Even after remission some symptoms of depression may still be present (residual symptoms).
Being depressed and not responding to treatment or relapsing is a terribly difficult situation. The patients are suffering and nothing appears to work to relieve their intense depression. Suicide becomes a real possibility. So, it is imperative that other treatments be identified that can relieve the suffering. Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) was specifically developed to treat depression. MBCT involves mindfulness training, containing sitting, walking and body scan meditations, and cognitive therapy that is designed to alter how the patient relates to the thought processes that often underlie and exacerbate psychological symptoms. MBCT has been shown to be effective for the treatment of major depression. But there is little understanding of the cost-effectiveness of MBCT relative to drug treatment. So, it is important to take a serious look at the costs of implementing MBCT and its effectiveness in comparison to the costs and effectiveness of antidepressant pharmacotherapy.
In today’s Research News article “Cost-Utility Analysis of Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy Versus Antidepressant Pharmacotherapy for Prevention of Depressive Relapse in a Canadian Context. Canadian journal of psychiatry” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7492890/ ) Pahlevan and colleagues reviewed published research studies comparing the cost-effectiveness of Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) versus antidepressant pharmacotherapy for the prevention of relapse in patients with Major Depressive Disorder who had had at least 2 past episodes of major depression.
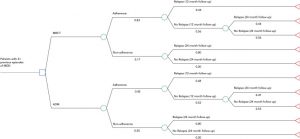
They report that the published research found that over a 2-year period Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) costs $2,224.67 less than antidepressant pharmacotherapy and produces greater gains in quality of life. This greater cost effectiveness of MBCT disappeared when adherence rates were considered. Hence, the greater cost effectiveness of MBCT was due to its ability to motivate greater compliance with the treatment.
These results are important as when multiple effective treatments are available, the cost of treatment becomes important. The analysis suggests that Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) not only costs less to deliver but also produces greater benefits. It is interesting that this advantage over antidepressant pharmacotherapy was due to improved compliance and not the superiority of the treatment. But a treatment is only as good as the patient’s adherence to its requirements and MBCT produces greater adherence.
So, mindfulness is a cost-effective treatment to prevent depression relapse.
“The rationale behind the MBCT program is based on an empirically supported, theoretical framework suggesting that patients with recurrent depression become more vulnerable to developing depression as cognitive reactivity increases.” – Marloes J Huijbers
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are also available on Google+ https://plus.google.com/106784388191201299496/posts and on Twitter @MindfulResearch
Study Summary
Pahlevan, T., Ung, C., & Segal, Z. (2020). Cost-Utility Analysis of Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy Versus Antidepressant Pharmacotherapy for Prevention of Depressive Relapse in a Canadian Context: Analyse coût-utilité de la thérapie cognitive basée sur la pleine conscience contre la pharmacothérapie antidépressive pour prévenir la rechute de la dépression en contexte canadien. Canadian journal of psychiatry. Revue canadienne de psychiatrie, 65(8), 568–576. https://doi.org/10.1177/0706743720904613
Abstract
Objective:
Patients suffering from major depressive disorder (MDD) experience impaired functioning and reduced quality of life, including an elevated risk of episode return. MDD is associated with high societal burden due to increased healthcare utilization, productivity losses, and suicide-related costs, making the long-term management of this illness a priority. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT), a first-line preventative psychological treatment, compared to maintenance antidepressant medication (ADM), the current standard of care.
Method:
A cost–utility analysis was conducted over a 24-month time horizon to model differences between MBCT and ADM in cost and quality-adjusted life years (QALY). The analysis was conducted using a decision tree analytic model. Intervention efficacy, utility, and costing data estimates were derived from published sources and expert consultation.
Results:
MBCT was found to be cost-effective compared to maintenance ADM over a 24-month time horizon. Antidepressant pharmacotherapy resulted in 1.10 QALY and $17,255.37 per patient on average, whereas MBCT resulted in 1.18 QALY and $15,030.70 per patient on average. This resulted in a cost difference of $2,224.67 and a QALY difference of 0.08, in favor of MBCT. Multiple sensitivity analyses supported these findings.
Conclusions:
From both a societal and health system perspective, utilizing MBCT as a first-line relapse prevention treatment is potentially cost-effective in a Canadian setting. Future economic evaluations should consider combined treatment (e.g., ADM and psychotherapy) as a comparator and longer time horizons as the literature advances.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7492890/