Meditation Alters a Variety of Biological Mechanisms and Improves Mental Disorders
By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
“Meditation-which come in many variations-has long been acknowledged as a tool to master the mind and cope with stress. Science is increasingly validating those claims, especially for depression, schizophrenia, anxiety, PTSD (post-traumatic stress disorder), and ADHD (attention deficit hyperactivity disorder).” – Mental Health America
Meditation training has been shown to improve health and well-being. It has also been found to be effective for a large array of medical and psychiatric conditions, either stand-alone or in combination with more traditional therapies. There are a number of ways that meditation practices produce these benefits, including changes to the brain and physiology. It is useful to review and summarize what has been discovered regarding the mechanisms by which meditation practice improves mental disorders.
In today’s Research News article “Biological mechanism study of meditation and its application in mental disorders.” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7359050/) Shen and colleagues review and summarize the published scientific research studies on the mechanisms by which meditation practice improves mental disorders.
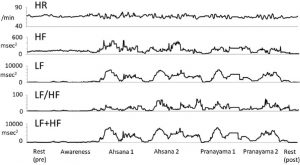
They report that the published research has found complex and widespread changes in the nervous system occur as a result of meditation. In the central nervous system these are relatively long lasting changes in the amount and connectivity of the brain tissue, termed neuroplastic changes, and these may underlie the beneficial changes in the meditators. In addition, meditation appears to alter the peripheral nervous system, in particular, the autonomic nervous system. Meditation increases parasympathetic activity that underlies vegetative functions and relaxation. This may be one mechanism by which meditation improves stress responses.
They further report that the published research found that meditation improves the functions of the immune and inflammatory systems. These effects also improve stress responses and fighting off disease. Hence, the effects of meditation on these biological process may underlie meditations ability to improve health. Since inflammatory responses often accompany mental illnesses, this may also be a mechanism by which meditation improved mental disease.
On a genetic, microbiological, level meditation has been found to alter the expression of genes that promote health. This may be the underlying reason that meditation improves the immune and inflammatory systems. Also, on the genetic level the research has found that meditation promotes the preservation of telomeres. These are the ends of the chromosomes that shorten throughout the lifetime and are thought to perhaps underlie cellular aging. This mechanism may underlie meditation’s ability to slow the aging process.
Meditation has been found through systematic controlled research to improve a wide array of mental illnesses. These include depression, including major depressive disorders, Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), and Schizophrenia. In addition, meditation has been found to aid in recovery from substance abuse disorders and to help prevent relapse.
It is clear from the published scientific research that meditation alters a wide array of physiological processes and improves and improves an equally wide array of mental illnesses. It will be important in the future to link the two to begin to understand what physiological changes underlie which improvements in mental illness. Regardless it is clear that meditation has many beneficial effects that promote physical and mental well-being.
So, practice meditation to alter a variety of biological mechanisms and improve mental disorders.
“Mindfulness exercises are valuable and useful for anyone, but most especially for people who are struggling with mental illness or addictions. “ – Sarah Levin
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are also available on Google+ https://plus.google.com/106784388191201299496/posts and on Twitter @MindfulResearch
Study Summary
Shen, H., Chen, M., & Cui, D. (2020). Biological mechanism study of meditation and its application in mental disorders. General psychiatry, 33(4), e100214. https://doi.org/10.1136/gpsych-2020-100214
Abstract
In recent years, research on meditation as an important alternative therapy has developed rapidly and been widely applied in clinical medicine. Mechanism studies of meditation have also developed progressively, showing that meditation has great impact on brain structure and function, and epigenetic and telomere regulation. In line with this, the application of meditation has gradually been expanded to mental illness, most often applied for major depressive disorders and substance-related and addictive disorders. The focus of this paper is to illustrate the biological mechanisms of meditation and its application in mental disorders.
Conclusions
Over the past two decades, meditation has been used in a great variety of fields to relieve stress, regulate emotions and promote physical and mental health. In recent years, the application of meditation in the psychiatric field has gradually received attention. It has become an adjunctive and alternative therapy for depression, PTSD and ADHD and has been carried out for the acute and remission stages of treatment for severe schizophrenia. Additionally, it can ameliorate emotional distress, craving and withdrawal symptoms in substance addiction. However, the current researchers adopt different meditation methods and diverse training durations, which leads to the inability to systematically evaluate which type of meditation is more beneficial to which populations or diseases, and to completely elucidate the biological mechanism of meditation. In the future, further targets for selective meditation subtypes along with prescribed training time, and randomised controlled studies with sufficient samples are required to determine the efficacy of meditation on the one hand, and simultaneously study the mechanisms behind meditation on the mind–body interaction, which can better display the positive function of meditation as an ancient physical and mental healing method in promoting human health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7359050/