Improve Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) with Mindfulness
By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
“Overall, there is a lot of evidence supporting mindfulness as a treatment approach for adults with PTSD, and a recent burgeoning literature corroborating positive neurological changes is following suit.” – Jennifer Wolkin
Experiencing trauma is quite common. It has been estimated that 60% of men and 50% of women will experience a significant traumatic event during their lifetime. But, only a fraction will develop Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). But this still results in a frightening number of people with 7%-8% of the population developing PTSD at some point in their life. For military personnel, it’s much more likely for PTSD to develop with about 11% – 20% of those who have served in a war zone developing PTSD.
PTSD involves a number of troubling symptoms including reliving the event with the same fear and horror in nightmares or with a flashback. PTSD sufferers avoid situations that remind them of the event this may include crowds, driving, movies, etc. and may avoid seeking help because it keeps them from having to think or talk about the event. They often experience negative changes in beliefs and feelings including difficulty experiencing positive or loving feelings toward other people, avoiding relationships, memory difficulties, or see the world as dangerous and no one can be trusted. Sufferers may feel hyperarousal, feeling keyed up and jittery, or always alert and on the lookout for danger. They may experience sudden anger or irritability, may have a hard time sleeping or concentrating, may be startled by a loud noise or surprise.
Obviously, these are troubling symptoms that need to be addressed. There are a number of therapies that have been developed to treat PTSD. One of which, mindfulness training has been found to be particularly effective. Mindfulness Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) has been found to improve PTSD symptoms. It has been shown that mindfulness practices can alter the brain structures and connectivity and this may underlie the beneficial effects of mindfulness on PTSD.
In today’s Research News article “Mindfulness-based treatments for posttraumatic stress disorder: a review of the treatment literature and neurobiological evidence.” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5747539/ ), Boyd and colleagues review and summarize the published research literature on the effects of mindfulness training on the brain and its relationship to improvements in PTSD symptoms. They report that there is substantial evidence that a variety of mindfulness-based treatments including Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR), Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT), and Loving Kindness Meditation are effective for relieving the symptoms of PTSD.
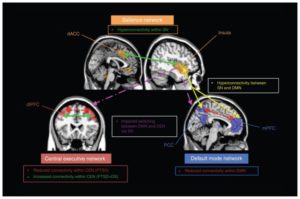
In regards to brain function, they report that mindfulness practices result in greater activity in the prefrontal cortex, structures that are involved in higher level thought processes and attention and lower activity in the amygdala region that is associated with emotional arousal. In addition, there is increased connectivity between these two regions. This could explain the ability of mindfulness practices to reduce hyperarousal and emotionality with more rational thought and improvement in emotional regulation. In addition, they report that a series of midline cortical structures labelled the default mode network (DMN) have increased connectivity, suggesting an improvement in self-referential thinking.
There is increased activity in a series of cortical structures that connect to lower centers in the brain labelled the salience network (SN) that appears to be involved in detecting particularly important stimuli and regulating emotional responses to them. This may result in the PTSD sufferer having a greater ability to respond appropriately to things in the environment that may have previously produced flashbacks and hyperarousal. Finally, mindfulness training appears to improve the activity and connectivity of the brain’s Central Executive Network (CEN), including dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and the posterior parietal cortex, that is associated with high level thinking.
These findings suggest that mindfulness training alters brain function to increase thinking and reasoning in contrast to emotional arousal. This is exactly what the PTSD patient needs as PTSD tends to produce the opposite pattern with decreased reasoning and increased emotional responding. Hence these findings suggest that mindfulness training acts on the nervous system to counter the abnormal brain responses that occur with PTSD and thereby relieve the symptoms of PTSD. Obviously much more research is needed. But a coherent picture is emerging of the alterations in the nervous system produced by mindfulness training that are responsible for its beneficial effects on the symptoms of PTSD.
So, improve post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) with mindfulness.
“This type of attention training may help patients notice when they are stuck in a negative pattern of thought or rumination and make it a little easier to shift their attention to other things. And if you think about what mindfulness meditation is, that makes perfect sense. The ‘muscle’ that you are training is the ability to catch yourself when you are not thinking about your breath and move it to something else.” – Tony King
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are also available on Google+ https://plus.google.com/106784388191201299496/posts and on Twitter @MindfulResearch
Study Summary
Jenna E. Boyd, Ruth A. Lanius, Margaret C. McKinnon. Mindfulness-based treatments for posttraumatic stress disorder: a review of the treatment literature and neurobiological evidence. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2018 Jan; 43(1): 7–25. Published online 2017 Oct 3. doi: 10.1503/jpn.170021
Abstract
Mindfulness-based treatments for posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) have emerged as promising adjunctive or alternative intervention approaches. A scoping review of the literature on PTSD treatment studies, including approaches such as mindfulness-based stress reduction, mindfulness-based cognitive therapy and metta mindfulness, reveals low attrition with medium to large effect sizes. We review the convergence between neurobiological models of PTSD and neuroimaging findings in the mindfulness literature, where mindfulness interventions may target emotional under- and overmodulation, both of which are critical features of PTSD symptomatology. Recent emerging work indicates that mindfulness-based treatments may also be effective in restoring connectivity between large-scale brain networks among individuals with PTSD, including connectivity between the default mode network and the central executive and salience networks. Future directions, including further identification of the neurobiological mechanisms of mindfulness interventions in patients with PTSD and direct comparison of these interventions to first-line treatments for PTSD are discussed.