Reduce Blood Pressure and Improve Vigilance with Yogic Alternative Nostril Breathing
By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
“Alternate Nostril Breathing helps calm the mind, reduce anxiety, and bring a feeling of relaxation to the entire body.” – Art of Living
Yoga practice is becoming increasingly popular in the west, for good reason. It has documented benefits for the individual’s psychological and physical health and well-being. It has also been shown to have cognitive benefits, improving memory. Yoga, however, consists of a number of components including, poses, breathing exercises, meditation, concentration, and philosophy/ethics. So, it is difficult to determine which facet or combination of facets of yoga are responsible for which benefit. Hence, it is important to begin to test each component in isolation to determine its effects.
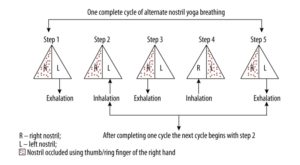
Alternate nostril yoga breathing is a regulated breathing alternating between the left and right nostril. Breathing through each nostril is thought to affect its respective hemisphere in the brain producing differential effects. In today’s Research News article “Alternate-Nostril Yoga Breathing Reduced Blood Pressure While Increasing Performance in a Vigilance Test.” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5755948/ ), Telles and colleagues recruited male college students and had them practice either Alternate-Nostril Yoga Breathing, Breath Awareness, or quiet rest for 18 minutes on three separate days in random order. The participants were measured before and after each practice for blood pressure and vigilance. To measure vigilance, they had the participants perform a digit vigilance test in which they were asked to cancel the numbers 6 and 9 from a page of 1500 random digits and recorded the time to complete the task and the number of errors made.
They found that compared to baseline and the control conditions of breath awareness and quiet sitting there was a significant reduction in systolic and arterial blood pressure following alternate nostril breathing. They also found that after alternate nostril breathing there was a significant reduction in the time to complete the vigilance task. But, this was also true for the quiet sitting condition. Hence, alternate nostril breathing appears to reduce the level of activation and improve vigilance. But, the improvement in vigilance may be simply due to the rest provided by the task. This suggests that yoga practice has its beneficial effects, in part, by the ability of the breathing practices to reduce physiological activation.
So, reduce blood pressure and improve vigilance with yogic alternative nostril breathing.
“Alternate Nostril Breathing: This simple yet most powerful technique is a pranayama that is easy to do, and it creates a deep sense of well-being and harmony on the physical, mental, and emotional levels. It is integrating and grounding, and balances the right and left hemispheres of the brain.” – Yogi Bhajan
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are also available on Google+ https://plus.google.com/106784388191201299496/posts and on Twitter @MindfulResearch
Study Summary
Shirley Telles, Sadhana Verma, Sachin Kumar Sharma, Ram Kumar Gupta, Acharya Balkrishna. Alternate-Nostril Yoga Breathing Reduced Blood Pressure While Increasing Performance in a Vigilance Test. Med Sci Monit Basic Res. 2017; 23: 392–398. Published online 2017 Dec 29. doi: 10.12659/MSMBR.906502
Abstract
Background
Reports suggest that vigilance or sustained attention increases sympathetic activity. A persistent increase in sympathetic activity can lead to an increase in blood pressure. Alternate-nostril yoga breathing has been shown to be useful to (i) improve attention and (ii) decrease the systolic and diastolic blood pressure. Earlier studies did not report simultaneous recordings of the blood pressure and performance in vigilance tests after alternate-nostril yoga breathing. With this background, the present study was planned to determine if 15 minutes of alternate nostril yoga breathing could improve the performance in a vigilance test without an increase in blood pressure.
Material/Methods
Fifteen healthy male volunteers participated in the study (group mean age ±SD, 22.4±2.4 years). Participants were assessed on 3 separate days in 3 different sessions. These were (i) alternate nostril yoga breathing, (ii) breath awareness, and (iii) sitting quietly as a control. Blood pressure and the digit vigilance test were simultaneously assessed before and after each session.
Results
Systolic blood pressure (p<0.01), mean arterial blood pressure (p<0.05), and the time taken to complete the digit vigilance test (p<0.05) significantly decreased following alternate-nostril yoga breathing. The time taken to complete the digit vigilance test differed significantly between sessions (p<0.05). The time taken to complete the digit vigilance test was also significantly decreased after sitting quietly (p<0.01).
Conclusions
Alternate-nostril yoga breathing appears to improve performance in the digit vigilance test, along with a reduction in systolic blood pressure. This is suggestive of better vigilance without sympathetic activation.