Produce Lasting Improvements in Resilience and Well-Being in Pre-Retirement Employees with Mindfulness
By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
“workers who took the mindfulness class reported feeling much better. They had less prolonged fatigue — that feeling of exhaustion that doesn’t go away even after having a chance to rest. They also felt less stressed, reported reduced anxiety and depression, and had fewer sleep difficulties, aches and pains, and problems getting along with others.” – Ronald Siegel
Work is very important for our health and well-being. We spend approximately 25% of our adult lives at work. How we spend that time is immensely important for our psychological, social, and physical health. But nearly 2/3 of employees worldwide are unhappy at work. This is partially due to work-related stress which is epidemic in the western workplace. Almost two thirds of workers reporting high levels of stress at work. This stress can result in impaired health and can result in burnout; producing fatigue, cynicism, and professional inefficacy. This can lead to early retirement.
To help overcome unhappiness, stress, and burnout, mindfulness practices have been implemented in the workplace. Indeed, mindfulness practices have been shown to markedly reduce the physiological and psychological responses to stress. As a result, it has become very trendy for business to incorporate meditation into the workday to help improve employee well-being, health, and productivity. These programs attempt to increase the employees’ mindfulness at work and thereby reduce stress. It is not known whether mindfulness will be similarly effective for older employees who are approaching retirement.
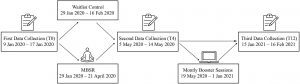
In today’s Research News article “Pre-retirement Employees Experience Lasting Improvements in Resilience and Well-Being After Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction.” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.699088/full?utm_source=F-AAE&utm_medium=EMLF&utm_campaign=MRK_1684212_a0P58000000G0YfEAK_Psycho_20210720_arts_A ) Diachenko and colleagues recruited active employees between the ages of 60-65 years and randomly assigned them to either receive an 8-week program of Mindfulness-Based Stress reduction (MBSR) or to a wait-list control condition. MBSR was delivered in weekly 2.5-hour sessions consisting of meditation, body scan, and yoga along with group discussion and daily 45 minute home practice. After training the participants received monthly 2-hour booster sessions delivered online. They were measured before and after training and 12 months later for perceived stress, resilience, well-being, distress, anxiety, depression, satisfaction with life, quality of thoughts and feelings at rest, and prior experience with yoga and meditation.
They found that in comparison to baseline and the wait-list controls, the participants who received Mindfulness-Based Stress reduction (MBSR) had significantly higher levels of resilience, well-being, and comfort in their thoughts at rest, and lower levels of sleepiness that were still significant 12 months later. These findings suggest that MBSR training improves the psychological health of older employees nearing retirement.
Mindfulness training has been shown in past research to improve resilience, well-being, and sleep. So, these findings are not surprising. What is new here is that these improvements in psychological health occurred in individuals approaching retirement and these improvements lasted for at least a year after training. It is possible, but not measured, that these improvements may lead to the employees staying in their jobs longer before retirement.
So, produce lasting improvements in resilience and well-being in pre-retirement employees with mindfulness.
“The most vital parts of mindfulness come not from positive thinking and meditation alone but the business’s approach to its employees.” – Forbes
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are also available on Google+ https://plus.google.com/106784388191201299496/posts and on Twitter @MindfulResearch
Study Summary
Diachenko M, Smith KK, Fjorback L, Hansen NV, Linkenkaer-Hansen K and Pallesen KJ (2021) Pre-retirement Employees Experience Lasting Improvements in Resilience and Well-Being After Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction. Front. Psychol. 12:699088. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.699088
The socio-economic benefits of interventions to prevent stress and related mental health problems are enormous. In the labor market, it is becoming desirable to keep employees for as long as possible. Since aging implies additional stressors such as increased risk of illness, and added pressure by professional tasks such as transferring knowledge, or learning new technologies, it is of particular relevance to offer stress-reduction to pre-retirement employees. Here, we report the effects of an eight-week Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) intervention on mental well-being in 60–65-year-old work-active Danish employees, compared to a waiting-list control group. We observed improvements in resilience (Brief Resilience Scale) and mental well-being (WHO-5) not only at the end of the intervention, but also at the 12-month follow-up measurement that was preceded by monthly booster sessions. Interestingly, whereas well-being usually refers to experiences in the past weeks or months, we observed increasing Comfort in the MBSR-intervention group during a 5-minute eyes-closed rest session suggesting that this therapeutic effect of MBSR is measurable in how we feel even during short periods of time. We argue that MBSR is a cost-effective intervention suited for pre-retirement employees to cultivate resilience to prevent stress, feel more comfortable with themselves, maintain a healthy work-life in the last years before retirement, and, potentially, stay in their work-life a few more years than originally planned.