Reduce the Symptoms of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) with Mindfulness
By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
“Normally I would have lost my keys and then gone tearing through the house looking for them. ( . . . ) And then ( . . . ) completely losing yourself in that. And these days that just doesn’t happen anymore. When I lose something now it’s more like, “okay, then let’s just look for it,” and I go and stand calmly in my room and then at some point I find it.” – Study Participant
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is most commonly found in children, but for about half it persists into adulthood. It’s estimated that about 5% of the adult population has ADHD. Hence, this is a very large problem that can produce inattention, impulsivity, hyperactivity, and emotional issues, and reduce quality of life. The most common treatment is drugs, like methylphenidate, Ritalin, which helps reducing symptoms in about 30% of the people with ADHD. Unfortunately, the effectiveness of the drugs appears to be markedly reduced after the first year. In addition, the drugs often have troublesome side effects, can be addictive, and can readily be abused. So, drugs, at present, do not appear to be a good solution, only affecting some, only for a short time, and with unwanted side effects.
There are indications that mindfulness practices may be an effective treatment for ADHD. It makes sense that it should be, as the skills and abilities strengthened by mindfulness practices are identical to those that are defective in ADHD, attention, impulse control, executive function, emotion control, and mood improvement. In addition, unlike drugs, they are relatively safe interventions that have minimal troublesome side effects. Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) is a mindfulness practice that contains Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and assigned homework. During therapy the patient is trained in mindfulness and to investigate and alter aberrant thought patterns.
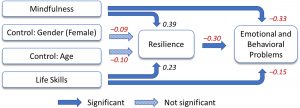
In today’s Research News article “The Feasibility, Effectiveness, and Process of Change of Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy for Adults With ADHD: A Mixed-Method Pilot Study.” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7081523/), Janssen and colleagues recruited adults diagnosed with ADHD who had completed an 8-week program of Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT). Training occurred in weekly 2.5-hour sessions along with 30 minutes per day of home practice. They were measured before and after training for mindfulness, Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) symptoms, behavioral regulation, metacognition, self-compassion, general functioning, and health status. They also participated in a focus group 3 months after training.
Only 16% of the patients failed to complete training. They found that in comparison to baseline, following Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) training there were significant increases in mental health, self-compassion, total executive functioning, including metacognition including the self-monitor, working memory, plan/organize, task monitor and organization of materials subscales and significant reductions in total ADHD symptoms, including inattention and hyperactive-impulsive symptoms. The analysis of the focus group data indicated that the participants believed that they improved due to increased ability to self-regulate.
Although this study did not have a comparison, control, condition, the results are similar to those found in prior controlled studies that mindfulness training improves the symptoms of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). The study demonstrated that Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) training was feasible and acceptable for the treatment of adult patients with ADHD and that the treatment improved their symptoms, mental health, cognitive ability, and the patients’ ability to regulate their own behavior.
So, reduce the symptoms of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) with mindfulness.
“I can spend the whole day in a haze, but when we focus consciously on our breathing, I’m able to turn it around. I also have that during meetings or discussions. If I’ve had enough at a certain point and I notice my mind wandering off, I think about the breathing and I’m able to be more present again.” – Study Participant
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are also available on Google+ https://plus.google.com/106784388191201299496/posts and on Twitter @MindfulResearch
Study Summary
Janssen, L., de Vries, A. M., Hepark, S., & Speckens, A. (2020). The Feasibility, Effectiveness, and Process of Change of Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy for Adults With ADHD: A Mixed-Method Pilot Study. Journal of attention disorders, 24(6), 928–942. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087054717727350
Abstract
Objective: Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) is a promising psychosocial intervention for adult ADHD. The feasibility and effectiveness of an adapted MBCT program is explored, together with the possible process of change. Method: Mixed-method study with 31 ADHD patients participating in an adapted MBCT program. Self-report questionnaires on ADHD symptoms, executive functioning, mindfulness skills, self-compassion, patient functioning, and health status were administered before and after MBCT. Semi-structured interviews were conducted with 24 patients. Results: A modest drop-out of n = 5 (16%) was found. MBCT resulted in a significant reduction of ADHD symptoms and improvements of executive functioning, self-compassion, and mental health. Qualitative analysis provided insight in facilitators and barriers participants experienced, and their process of change. Conclusion: The adapted MBCT program seemed to be feasible for adults with ADHD and preliminary evidence for the effectiveness is shown. An adequately powered Randomized Controlled Trial (RCT) is needed to further examine the effectiveness of MBCT for ADHD.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7081523/