Mindfulness is Associated with Greater Resilience and Less Emotional and Behavioral Problems in Adolescents
By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
“mindfulness practice could be beneficial to teens, helping them cultivate empathy, as well as skills for concentration and impulse control. In short, mindfulness can help adolescents navigate the challenges of adolescence.” – Sarah Rundell Beach
Adolescence is a time of mental, physical, social, and emotional growth. It is during this time that higher levels of thinking, sometimes called executive function, develops. But adolescence can be a difficult time, fraught with challenges. During this time the child transitions to young adulthood; including the development of intellectual, psychological, physical, and social abilities and characteristics. There are so many changes occurring during this time that the child can feel overwhelmed and unable to cope with all that is required. This can lead to emotional and behavioral problems.
Indeed, up to a quarter of adolescents suffer from depression or anxiety disorders, and an even larger proportion struggle with subclinical symptoms. Mindfulness training in adults has been shown to reduce anxiety and depression levels and improve resilience and emotional regulation. In addition, in adolescents it has been shown to improve emotion regulation and to benefit the psychological and emotional health.
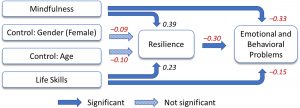
In today’s Research News article “Mindfulness, Life Skills, Resilience, and Emotional and Behavioral Problems for Gifted Low-Income Adolescents in China.” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.00594/full?utm_source=F-AAE&utm_medium=EMLF&utm_campaign=MRK_1293822_69_Psycho_20200407_arts_A), Huang and colleagues recruited low-income gifted high school students and measured them for emotional and behavioral problems, including both internalizing and externalizing behaviors, resilience, life skills, including self-control, assertiveness, refusal and relaxation, and mindfulness.
They found that the higher the levels of mindfulness the higher the levels of resilience and life skills and the lower the levels of emotional and behavioral problems. They also found that the higher the levels of life skills the higher the levels of mindfulness and resilience and the lower the levels of emotional and behavioral problems. Structural modelling revealed that mindfulness and life skills were associated with reduced emotional and behavioral problems both directly and indirectly by being associated with higher levels of resilience that was in turn associated with lower levels of emotional and behavioral problems.
These results are interesting but correlational and as such causation cannot be determined. Nevertheless, they suggest that the emotional and behavioral problems of gifted adolescents from low-income families are to some extent reduced by having strong mindfulness, resilience, and life skills. Additionally, the findings suggest that mindfulness and life skills are not only directly related to less emotional and behavioral problems but also indirectly by being related to higher levels of resilience. It remains for future research to determine if these connections are causal by training adolescents in mindfulness and life skills and observing if there are increases in resilience and decreases in emotional and behavioral problems.
So, mindfulness is associated with greater resilience and less emotional and behavioral problems in adolescents.
“Mindfulness processes and practices can help young people develop emotional resilience, self-awareness and regulation skills that assist them in taking greater responsibility for their behaviors, decisions and relationships.” – Jennifer Frank
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are also available on Google+ https://plus.google.com/106784388191201299496/posts and on Twitter @MindfulResearch
Study Summary
Huang C-C, Chen Y, Jin H, Stringham M, Liu C and Oliver C (2020) Mindfulness, Life Skills, Resilience, and Emotional and Behavioral Problems for Gifted Low-Income Adolescents in China. Front. Psychol. 11:594. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.00594
In contrast to emotional and behavioral problems (EBPs), which can disrupt normal adolescent development, resilience can buffer the effects of stress and adverse childhood experiences and can help youth overcome adversity. While research has looked at the relationship between adolescent resilience and EBPs, current literature relatively lack a discussion of a strengths-based approach of resilience framework, nor discuss non-western sociocultural contexts. In this study, we utilized the resilience theory to examine the effects of individual mindfulness and life skills on resilience and consequently on EBPs in a group of low-income and gifted adolescents in China. A secondary data of 152 adolescents from a specialized school for low-income and gifted students in Guangzhou, China was used for the analysis. The findings from structural equation modeling indicated that mindfulness and life skills were associated with heightened resilience and reduced EBPs. In addition, resilience reduced EBPs for this group of adolescents. These findings underscore the promise of mindfulness and life skills training on increasing resilience and reducing EBPs in gifted adolescents.