Increase Brain Grey Matter with Mindfulness
By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
“meditating can give you the brain of a 25-year-old. Too bad it can’t also give you the body of one.” – Melanie Curtain
Mindfulness training has been shown through extensive research to be effective in improving physical and psychological health and particularly with reducing the physical and psychological reactions to stress. There are a number of ways that meditation practices produce these benefits, including changes to the brain and physiology. The nervous system changes in response to how it is used and how it is stimulated in a process called neuroplasticity. Highly used areas grow in size, metabolism, and connectivity. Mindfulness practices in general are known to produce these kinds of changes in the structure and activity of the brain. The research has been accumulating and there is a need to summarize what has been learned.
In today’s Research News article “Mindfulness related changes in grey matter: a systematic review and meta-analysis.” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8500886/ ) Pernet and colleagues review, summarize, and perform a meta-analysis of the published research on the effects of mindfulness practices on the amount of grey matter in the brain and brain structures.
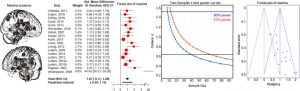
They identified 25 published research studies that included a total of 1406 participants. They report that the published research found that meditation practice produced an enlargement of the insular cortex. There was also increased functional connectivity between the insular cortex and the cingulate cortex and the paracingulate gyrus. They note that there was great variation in the studies in terms of other structures showing increases in size and connectivity but little commonality. The studies, however, very greatly in procedure, meditation practice and experience, participant types, and numbers, etc. So, they recommend that future studies be more standardized and with larger numbers of participants.
With this heterogeneity of studies, finding that the insular cortex is expanded in most highlights its importance in meditation effects on the brain. The insular cortex is a highly connected structure of the brain that is so interconnected with multiple other brain areas that it has been thought of as a hub. It has been implicated in interoception, multimodal sensory processing, autonomic control, perceptual self-awareness, and emotional guidance of social behavior. This makes sense as meditation practice involves the perception of the internal state derived from multiple sensory experiences and, of course, self-awareness. The research findings suggest that meditation produces neuroplastic changes in the brain that are reflective of the mental states occurring in meditation. This, in turn, likely makes the practitioner more sensitive to these mental states.
So, increase brain grey matter with mindfulness.
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are available on Twitter @MindfulResearch
“mindfulness meditation induces gray matter plasticity, suggesting that structural changes in ventral PCC—a key hub associated with self-awareness, emotion, cognition, and aging—may have important implications for protecting against mood-related disorders and aging-related cognitive declines.” – Rongxiang Tang,
Study Summary
Pernet, C. R., Belov, N., Delorme, A., & Zammit, A. (2021). Mindfulness related changes in grey matter: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain imaging and behavior, 15(5), 2720–2730. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-021-00453-4
Abstract
Knowing target regions undergoing strfuncti changes caused by behavioural interventions is paramount in evaluating the effectiveness of such practices. Here, using a systematic review approach, we identified 25 peer-reviewed magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) studies demonstrating grey matter changes related to mindfulness meditation. An activation likelihood estimation (ALE) analysis (n = 16) revealed the right anterior ventral insula as the only significant region with consistent effect across studies, whilst an additional functional connectivity analysis indicates that both left and right insulae, and the anterior cingulate gyrus with adjacent paracingulate gyri should also be considered in future studies. Statistical meta-analyses suggest medium to strong effect sizes from Cohen’s d ~ 0.8 in the right insula to ~ 1 using maxima across the whole brain. The systematic review revealed design issues with selection, information, attrition and confirmation biases, in addition to weak statistical power. In conclusion, our analyses show that mindfulness meditation practice does induce grey matter changes but also that improvements in methodology are needed to establish mindfulness as a therapeutic intervention.