Mindfulness is Associated with Lower Stigma and Improved Social Engagement in Breast Cancer Survivors
By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
“Cancer is a word, not a sentence.”- John Diamond
Because of great advances in treatment, many patients today are surviving cancer. But cancer survivors frequently suffer from anxiety, depression, mood disturbance, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), sleep disturbance, fatigue, sexual dysfunction, loss of personal control, impaired quality of life, and psychiatric symptoms which have been found to persist even ten years after remission. Also, cancer survivors can have to deal with a heightened fear of reoccurrence.
Safe and effective treatments for the symptoms of cancer and the physical and psychological effects of the treatments are needed. Mindfulness training has been shown to help with general cancer recovery and mindfulness practices have been shown to improve the residual symptoms in cancer survivors. The mechanisms by which mindfulness may help cancer patients need to be explored.
Social engagement has positive benefits for cancer patients as they tend to improve the patient’s psychological well-being which, in turn, can reduce stress and the deleterious effects it has on the patient’s physical well-being. Unfortunately, there is a stigma around having cancer which can make the patient less likely to engage socially.
.In today’s Research News article “The mediator role of stigma in the association of mindfulness and social engagement among breast cancer survivors in China. Support Care Cancer.” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8861258/ ) Jiang and colleagues demonstrate that mindfulness is associated with greater social engagement and also with the patients having lower beliefs about the stigma surrounding the disease and this helps to improve social engagement.
So, in part, mindfulness may improve cancer patients’ psychological well-being by reducing their beliefs about cancer stigma and improving social engagement.
“Cancer cannot cripple love, it cannot shatter hope, it cannot conquer the spirit.” – Unknown
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are also available on Twitter @MindfulResearch
Study Summary
Jiang N, Zhang YX, Zhao J, Shi HY, Wang T, Jin W, Wang JW, Yu JM. The mediator role of stigma in the association of mindfulness and social engagement among breast cancer survivors in China. Support Care Cancer. 2022 Jun;30(6):5007-5015. doi: 10.1007/s00520-022-06882-1. Epub 2022 Feb 22. PMID: 35192056; PMCID: PMC8861258.
Abstract
Purpose
This study aims to explore the association between mindfulness and social engagement among Chinese breast cancer survivors (BCSs) and the mediator role of stigma in the relation of mindfulness and social engagement.
Methods
This cross-sectional study was conducted among 937 BCSs from March to April 2021 in Shanghai, China. Data were collected using the Mindful Attention Awareness Scale, the Stigma Scale for Chronic Illness 8-item version, and the index of social engagement. Descriptive statistics, independent-sample t-test, one-way ANOVA, and regression analyses were used to explore the role of stigma in the association of mindfulness and social engagement among Chinese BCSs.
Results
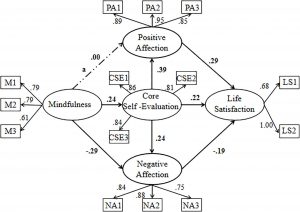
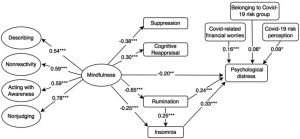
Social engagement levels differed significantly by participant’s BMI, education level, employment status, personal monthly income, monthly per capita household income. Mindfulness was positively correlated with social engagement, and stigma was negatively correlated with mindfulness and social engagement among Chinese BCSs. Stigma plays a complete mediating role in the relationship between mindfulness and social engagement in BCSs.
Conclusion
In the practice of individual mindfulness intervention on social engagement of BCSs, health care providers should identify and eliminate the constraints, which restrain the reduction of stigma level while individual mindfulness is being enhanced.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8861258/