By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
“Tai Chi Chuan, the great ultimate, strengthens the weak, raises the sick, invigorates the debilitated, and encourages the timid.” –Cheng Man-ch’ing
The aging process involves a systematic progressive decline in every system in the body, the brain included. The elderly frequently have problems with attention, thinking, and memory abilities, known as mild cognitive impairment. This is often a prelude to more severe decline such a dementia. An encouraging new development is that mindfulness practices such as meditation training and mindful movement practices can significantly reduce these declines in cognitive ability.
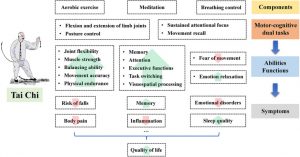
Tai Chi is an ancient Chinese practice involving mindfulness and gentle movements. It is easy to learn, safe, and gentle. Tai Chi has been practiced for thousands of years with benefits for health and longevity. Tai Chi training is designed to enhance function and regulate the activities of the body through controlled breathing, mindful concentration, and gentle movements. Only recently though have the effects of this practice been scrutinized with empirical research. This research has found that it is effective for an array of physical and psychological issues. It appears to strengthen the immune system, reduce inflammation and increase the number of cancer killing cells in the bloodstream, improve cardiovascular health, reduce arthritis pain, improve balance and reduce falls. It also appears to improve attentional ability improve cognitive ability in the elderly, and relieve depression.
In today’s Research News article “Mitigating effects and mechanisms of Tai Chi on mild cognitive impairment in the elderly.” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9906996/ ) Wang and colleagues review and summarize the published randomized controlled studies of the effects of Tai Chi practice on patients diagnosed with mild cognitive decline.
They report that Tai Chi practice relieved the symptoms of mild cognitive decline and delayed the onset of more severe dementia. The benefits include improved memory, executive function, and sleep and reduced body pain. They also report that Tai Chi practice appears to produce these benefits by altering the brain including increased brain volume, connectivity, and white matter efficiency and reduce inflammation.
Hence, the published research suggests that Tai Chi practice is an effective treatment for patients with mild cognitive impairment.
“The moment we believe that success is determined by an ingrained level of ability as opposed to resilience and hard work, we will be brittle in the face of adversity.” – Joshua Waitzkin
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are also available on the Contemplative Studies Blog http://contemplative-studies.org
Study Summary
Wang X, Si K, Gu W, Wang X. Mitigating effects and mechanisms of Tai Chi on mild cognitive impairment in the elderly. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Jan 6;14:1028822. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.1028822. PMID: 36760710; PMCID: PMC9906996.
Abstract
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is a major public health concern that endangers health and decreases the quality of life of the elderly around the world. A recent clinical guideline has recommended regular exercise (twice per week) for patients with MCI as part of an overall approach to management. Tai Chi, a form of light-to-moderate-intensity mind-body exercise, is particularly suitable for seniors. This review aims to summarize epidemiological studies related to the effects of Tai Chi on symptom remission in older adults with MCI and reveal the potential mechanisms. Evidence suggested that Tai Chi can improve cognitive functions and alleviate the accompanying symptoms of MCI in the elderly potentially by activating the expression of signals in different brain regions, altering their connectivity, increasing the brain volume, and modulating brain-derived neurotropic and inflammation factors. Studies comparing various types of Tai Chi may contribute to the identification of paradigms that have appropriate intensities and difficulty and exert good effects on older people with MCI. In addition, studies are warranted to determine the frequency and duration of training that can optimize the beneficial effects of Tai Chi on MCI.