The Noble Eightfold Path: Right Actions
By John M. de Castro, Ph.D/
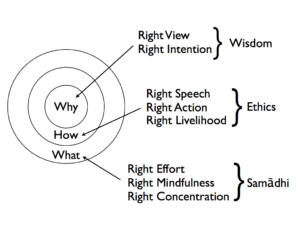
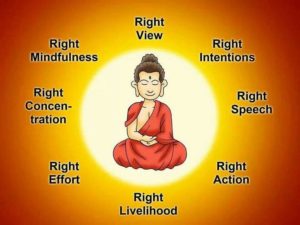
“Right Actions” is the fourth component of the Buddha’s Noble Eightfold Path, Right View, Right Intentions, Right Speech, Right Actions, Right Livelihood, Right Effort, Right Mindfulness and Right Concentration.” It follows directly from “Right View”. When one sees everything just as it is and understands how everything is impermanent and connected to everything else, that life involves suffering, that there are causes to that suffering, and that there is a way to escape from suffering, this leads directly to “Right Intention”, the aspiration to create greater happiness, wisdom, and well-being, and relieve suffering in ourselves and others. “Right Intention” then is the driver of “Right Actions,” actually engaging in activities that produce the desired results. “Right Actions” like all the components of the path is dependent upon and affects all the other components of the path.
In order to know what actions will actually produce greater happiness, wisdom, and well-being, and relieve suffering requires discernment dependent upon “Right View.” Without that understanding of how things really are we can easily take an action that we think will be productive only to find that it was destructive. On retreat, there are often participants who are crying and appearing to be distraught or in despair. Our initial instinct is to go to the individual and to try to console them and help them through their difficulties. But, that, in fact, will do more harm than good, preventing the individual from addressing the core problems that have arisen in retreat. Consoling them actually disrupts one of the beneficial aspects of retreat which allows deep and repressed issues to come forth, be experienced, accepted, and dealt with. In this case “Right Action” is to simply make sure that they are physically all right and leave them alone to work though their issues. On the surface, it seems cruel. But with discernment it can be seen that this will in the long run produce the relief of suffering.
There are some rather obvious “Right Actions” that are parts of most religious and moral teachings. These include not killing, stealing, sexual misconduct, lying, and abusing intoxicants. These are actually “Right Non-Actions.” The “Right Actions” would be protecting life, generosity, engaging in healthy loving sexual activities, truthfulness, and sobriety. The “Right Action” of telling the truth has been discussed with “Right Speech” and need not be repeated here. The present essay will focus of the other four.
Protecting life, not killing, means more than just protecting the lives of human beings. It extends to all sentient beings. We can have honest differences as to what constitutes a sentient being from all living things, to only humans, to some point in between. But taking the life of a sentient being produces suffering and deprives it of an opportunity to experience life and happiness. It would thus violate the “Right Intention” to promote greater happiness, wisdom, and well-being, and relieve suffering. If it can’t be determined which animals are sentient and which are not, then it would seem to be the best course for producing happiness and relieving suffering to err on the side of caution and refrain from killing any animal.
We need to protect our own life. Killing in self-defense is “Right Action” provided we have done everything possible to avoid it. Part of that self-defense is obtaining proper nourishment. It would seem reasonable that to eat, but not kill a sentient being, we should become vegetarian. But, the growing and producing of vegetables inevitably involves killing other animals. The process of harvesting crops inevitably results in the death of many rodents, birds, and reptiles. It is, in fact, virtually impossible to not in some way directly or indirectly produce or contribute to the death of animals in order to maintain one’s own life. Discernment tells us that trying our best to protect life and minimize the harm we might do in the process of preserving our own life is “Right Action.” The practical impossibility of being perfect leads to the conclusion that intention and effort to preserve life is the best we can do and that is enough.
Honoring the property of others, not stealing, means more than simply not taking what is not intentionally given. It also implies generosity. “Right Action” is giving freely of our time and resources where needed to promote happiness and relieve suffering. This could be volunteer work at an abused children’s shelter, monetary donations to the needy, or simply picking up groceries for an infirmed neighbor. We should not hoard our resources but share them generously. “Right Action” can also mean doing things to promote social justice. We obviously shouldn’t directly abuse the rights of others. Rather we should stand up and oppose the abuse of rights perpetrated by others or society. Hence “Right Action” could even include civil disobedience. Certainly, Mahatma Gandhi and Martin Luther King understood this. But they also understood that civil disobedience should occur only with care, deliberation, and discernment. “Right Action” demands our action, but, carefully considered action that isn’t motivated by anger, hatred, or revenge. In other words, we should not stand by as others rights are stolen. We should defend them, but do so in a responsible manner with “Right Intention.”
There has been immense harm caused to individuals, families, and society by sexual misconduct. It can have a devastating and permanent effects on the principals and those that surround them. It can produce lasting traumas, destroy families, and permanently scar children. It is no wonder that sexual misconduct is so important to prevent and sexual activity approached with “Right Actions.” This results in the prohibition of sexual activity by monastics. But, for the vast majority of people the middle way, between celibacy and licentiousness is called for. In other words, healthy loving sexual relations that is consensual and non-exploitive are “Right Actions.” The primary guiding principle is that the action produces greater harmony, happiness, wisdom, and well-being, and relieves suffering. So, engagement in sexual activity should be loving, caring, and sensitive, with the intention to produce good for all involved. That is right sexual action.
The “Right Action” of not abusing intoxicants, of sobriety, is also important as great harm can be done to the self and others by misuse of drugs and alcohol. The perils of alcoholism and the destructive power of drug addiction are well documented. But, the “Right Action” of sobriety extends to much lower levels of intoxicant use. To the extent that these substances can cloud the mind, impede judgment, and interfere with discernment, they can lead to improper or insensitive actions that can harm. So, “Right Action” calls for, if not complete prohibition, low level and judicious use of intoxicants. But, “Right Action” with intoxicants actually extends well beyond alcohol and drug to engaging in experiences that can induce harmful thinking and lead to wrong actions. This can include “ingesting” disturbing movies, books, TV shows, etc. that can induce disturbing thoughts and possibly even lead to wrong actions. “Right Action” calls for us to be careful what we consume to make sure that no matter what form it comes in, it is healthy and leads to happiness and well-being.
These are some specific and obvious “Right Actions.” Most actions are not so obvious. So “Right Action” calls for us to be vigilant and approach our behavior with discernment to insure, as best as possible, that our actions improve happiness and well-being and decrease suffering. But making the effort and spending the time and thoughtfulness involved in insuring that actions are “Right” can produce considerable benefits. It can make each of us and those around us happier, more content, and more fulfilled and less worried, anxious, and dissatisfied. Beyond its impact on everyday life, it can lead us to higher states as we pursue the eightfold path. Doing the “Right” thing sure has its advantages!
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are also available on Google+ https://plus.google.com/106784388191201299496/posts and on Twitter @MindfulResearch