Improve Cardiorespiratory Function in the Elderly with Tai Chi
By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
“Long term regular [Tai Chi] exercise has favourable effects on the promotion of balance control, flexibility, and cardiovascular fitness in older adults.” – Youlian Hong
The aging process involves a systematic progressive decline in every system in the body, the cardiovascular system and respiratory system included. The elderly frequently also have problems with attention, thinking, and memory abilities, known as mild cognitive impairment. An encouraging new development is that mindfulness practices such as meditation training and mindful movement practices can significantly reduce these declines.
Tai Chi has been practiced for thousands of years with benefits for health and longevity. Tai Chi training is designed to enhance function and regulate the activities of the body through regulated breathing, mindful concentration, and gentle movements. Tai Chi practice has been found to be effective for an array of physical and psychological issues. Tai Chi has been shown to help the elderly improve attention, balance, reducing falls, arthritis, cognitive function, memory, and reduce age related deterioration of the brain. The research on the effects of Tai Chi training on the cardiorespiratory system of older adults has been accumulating. So, it makes sense to summarize what has been learned.
In today’s Research News article “A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Tai Chi Training in Cardiorespiratory Fitness of Elderly People.” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8942636/ ) Tan and colleagues review and summarize the published research randomized controlled trials on the effects of Tai Chi training on the cardiorespiratory system of older adults (> 50 years of age). They identified 24 published research studies.
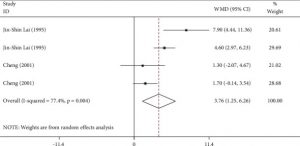
They report that the published randomized controlled trials found that Tai Chi training produced significant increases in heart rate, VO2 max (the maximum amount of oxygen your body can utilize during exercise) and O2 pulse (oxygen consumed per heart beat, a measure of stroke volume), and vital capacity (the greatest volume of air that can be expelled from the lungs after taking the deepest possible breath). The increase in vital capacity was significantly larger in participants who practiced for 48 weeks and over.
The results are clear. Tai Chi training produces improves cardiorespiratory function in older adults. Thus suggests that Tai Chi training can help overcome or delay age-related physical decline.
“tai chi is an effective way in improving cardiovascular responses and stress in prehypertensive individuals.” – Touraj Hashemi Nosrat-abad
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are also available on Twitter @MindfulResearch
Study Summary
Tan, T., Meng, Y., Lyu, J. L., Zhang, C., Wang, C., Liu, M., Zhao, X., Lyu, T., & Wei, Y. (2022). A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Tai Chi Training in Cardiorespiratory Fitness of Elderly People. Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine : eCAM, 2022, 4041612. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/4041612
Abstract
Objectives
The purpose of this study was to investigate the influence of Tai Chi on cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) in elderly people using meta-analysis.
Methods
This study used seven electronic databases and data retrieved from randomized controlled trials (RCTs) investigating the role of Tai Chi on CRF in the elderly. All these 24 RCTs were screened and selected from 7 literature databases. The Stata 11.2 software (StataCorp, USA) was used for the meta-analysis, subgroup analysis, and bias test, while the Cochrane Collaboration’s tool was used for the assessment of the risk of bias (RoB). 4 researchers independently participated in sample selection, data extraction, and RoB assessment.
Results
Following the inclusion criteria, 24 eligible studies were included in our analysis. The meta-analysis indicated that Tai Chi practice significantly increased the maximum rate of oxygen consumption (VO2 max) (weighted mean difference (WMD) = 3.76, 95% CI: 1.25 to 6.26, P < 0.1), leading to an overall reduction in the heart rate (HR) (WMD = −1.84, 95% CI: −2.04 to −1.63, P ≤ 0.001) and an increase in the O2 pulse (WMD = 0.94, 95% CI: 0.60 to 1.28, P ≤ 0.001) in individuals who practiced Tai Chi regularly compared with those who did not. The subgroup analysis suggested that overall in those who practiced Tai Chi, males (WMD = 1.48, 95% CI: 0.85 to 2.12, P ≤ 0.001) had higher O2 pulse than females (WMD = 0.73, 95% CI: 0.33 to 1.12, P ≤ 0.001). The subgroup analysis also showed an increase in the vital capacity (VC) (WMD = 316.05, 95% CI: 239.74 to 392.35, P ≤ 0.001) in individuals practicing Tai Chi. When the samples were further stratified by Tai Chi practicing time, the subgroup analysis suggested that individuals practicing Tai Chi over a period of 24 weeks showed no significant difference in VC (WMD = 82.95, 95% CI: -98.34 to 264.23, P=0.370), while those practicing Tai Chi over a period of 48 weeks showed a significant increase (WMD = 416.62, 95% CI: 280.68 to 552.56, P ≤ 0.001). Furthermore, the subgroup analysis demonstrated that the increase in VC is significantly correlated with the Tai Chi practicing time (WMD = 344.97, 95% CI: 227.88 to 442.06, P ≤ 0.001).
Conclusion
Regular Tai Chi practice could improve the CRF in the elderly, as indicated by significant improvement in indicators including VO2max, O2pulse, VC, and HR. However, gender and practice time might influence the overall beneficial outcomes.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8942636/