Depth of Meditation is Associated with Different Levels of Brain Electrical Activity
By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
“Neuroscientific studies, particularly EEG, are revealing much about the neural correlates of meditation in the hopes of understanding why it has therapeutic value, and as a way to probe the nature of self and consciousness.” – Aaron Nitzkin
Meditation training has been shown to improve health and well-being. It has also been found to be effective for a large array of medical and psychiatric conditions, either stand-alone or in combination with more traditional therapies. There are a number of ways that meditation practices produce these benefits, including changes to the brain and physiology. One way to observe the effects of meditation on neural activity is to measure changes in the electroencephalogram (EEG), the rhythmic electrical activity that can be recorded from the scalp.
The recorded activity can be separated into frequency bands. Delta activity consists of oscillations in the 0.5-3 cycles per second band. Theta activity in the EEG consists of oscillations in the 4-8 cycles per second band. Alpha activity consists of oscillations in the 8-12 cycles per second band. Beta activity consists of oscillations in the 15-25 cycles per second band while Gamma activity occurs in the 35-45 cycles per second band. Changes in these brain activities can be compared during different depths of meditation.
In today’s Research News article “Alpha and theta oscillations are inversely related to progressive levels of meditation depth.” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8633885/ ) Katyal and Goldin recruited healthy adult participants who were long-term meditators and demographically matched meditation naïve participants. They had their electroencephalogram (EEG) recorded during 4 blocks of either listening to a story, listening to music, or 2 6-minute blocks of meditation. They self-reported their depth of meditation after each block.
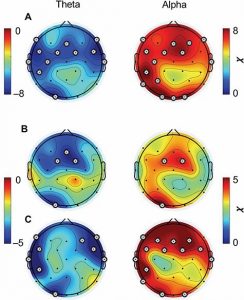
They found, not surprisingly, that in comparison to the meditation naïve participants, the experienced meditators had significantly greater depth of meditation. They also found that as the depth of meditation increased the alpha rhythm in the EEG significantly increased while the theta rhythm significantly decreased. This was true for both groups.
The alpha rhythm has been associated with relaxation and a suppression of mind wandering and distraction. Similarly, the greater the depth of meditation the less distraction and mind wandering. Thus, the increase in the alpha rhythm with increasing depth of meditation is reasonable and completely predictable. The theta rhythm is associated with dreaminess and sleep. That the theta rhythm is lowest with higher depths of meditation makes sense as depth is associated with alert awareness. Hence, the brain wave patterns seen during meditation are reflective of the depth of meditation.
So, depth of meditation is associated with different levels of brain electrical activity
“neurocognitive mechanisms that are present during both self-generated thought and controlled cognitive processes (i.e. the integration between the memory and executive components of cognition via alpha:theta cross-frequency coupling) are minimized during meditative practices.” – Julio Rodriguez-Larios
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are available on Twitter @MindfulResearch
Study Summary
Katyal, S., & Goldin, P. (2021). Alpha and theta oscillations are inversely related to progressive levels of meditation depth. Neuroscience of consciousness, 2021(1), niab042. https://doi.org/10.1093/nc/niab042
Highlights
- Our study reveals neurophysiological changes that occur as meditation experiences become deeper.
- Alpha and theta brainwaves are two reliable neurophysiological signatures of meditation.
- Theta activity increased with more distractions and was suppressed during deeper experiences.
- Increased alpha activity was related to fewer distractions and more deeper meditation experiences.
- Deeper meditation experiences appear to involve a suppression of executive neural processing.
Abstract
Meditation training is proposed to enhance mental well-being by modulating neural activity, particularly alpha and theta brain oscillations, and autonomic activity. Although such enhancement also depends on the quality of meditation, little is known about how these neural and physiological changes relate to meditation quality. One model characterizes meditation quality as five increasing levels of ‘depth’: hindrances, relaxation, concentration, transpersonal qualities and nonduality. We investigated the neural oscillatory (theta, alpha, beta and gamma) and physiological (respiration rate, heart rate and heart rate variability) correlates of the self-reported meditation depth in long-term meditators (LTMs) and meditation-naïve controls (CTLs). To determine the neural and physiological correlates of meditation depth, we modelled the change in the slope of the relationship between self-reported experiential degree at each of the five depth levels and the multiple neural and physiological measures. CTLs reported experiencing more ‘hindrances’ than LTMs, while LTMs reported more ‘transpersonal qualities’ and ‘nonduality’ compared to CTLs, confirming the experiential manipulation of meditation depth. We found that in both groups, theta (4–6 Hz) and alpha (7–13 Hz) oscillations were related to meditation depth in a precisely opposite manner. The theta amplitude positively correlated with ‘hindrances’ and increasingly negatively correlated with increasing meditation depth levels. Alpha amplitude negatively correlated with ‘hindrances’ and increasingly positively with increasing depth levels. The increase in the inverse association between theta and meditation depth occurred over different scalp locations in the two groups—frontal midline in LTMs and frontal lateral in CTLs—possibly reflecting the downregulation of two different aspects of executive processing—monitoring and attention regulation, respectively—during deep meditation. These results suggest a functional dissociation of the two classical neural signatures of meditation training, namely, alpha and theta oscillations. Moreover, while essential for overcoming ‘hindrances’, executive neural processing appears to be downregulated during deeper meditation experiences.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8633885/