Meditation on Different States of Consciousness Produces Different Brain Activity
By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
“Meditation is just self-directed neuroplasticity. In other words, you are directing the change of your brain by inwardly and consciously directing attention in a particular way. You’re using the mind to change the brain, like a child crafting a Playdough structure.” – Liam McClintock
Mindfulness training has been shown to improve health and well-being. It has also been found to be effective for a large array of medical and psychiatric conditions, either stand-alone or in combination with more traditional therapies. How exactly mindfulness practices produce their benefits is unknown. It is known that meditation practice alters states of consciousness and alters brain activity.
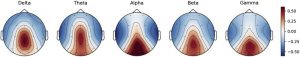
It is possible to investigate the relationships between consciousness and brain activity. One way is to measure changes in the electroencephalogram (EEG), the rhythmic electrical activity that can be recorded from the scalp. The recorded activity can be separated into frequency bands. Delta activity consists of oscillations in the 0.5-3 cycles per second band. Theta activity in the EEG consists of oscillations in the 4-8 cycles per second band. Alpha activity consists of oscillations in the 8-12 cycles per second band. Beta activity consists of oscillations in the 15-25 cycles per second band while Gamma activity occurs in the 35-45 cycles per second band. Changes in these brain activities can be compared during different forms of meditation with different conscious content.
In today’s Research News article “Large effects of brief meditation intervention on EEG spectra in meditation novices.” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7649620/ ) Stapleton and colleagues recruited healthy meditation-naïve adults and had them attend a 3-day meditation training workshop where seated meditation to music was practiced 3 times per day. The participants were instructed to focus on different states (emotions, gratitude, surrendering, emotions, future events, oneness, energy, future intentions, and moving energy) during the meditations. During before, during, and after each meditation brain activity was recorded with an electroencephalogram (EEG).
They found that from the baseline to the end of the meditations there was a significant global increase in both Theta (4-8 hz.) and Gamma (35-45 hz.) rhythms in the EEG. These activities normally occur during information processing in the brain. They also found that different meditations produced different patterns of EEG activity. Delta activity was increased to the greatest extent by meditations on gratitude, elevated emotions, and energy. Theta activity was increased to the greatest extent by meditations on gratitude, elevated emotions, and future intention. Alpha activity was increased to the greatest extent by meditations on gratitude, oneness, and future intention. Beta activity was increased to the greatest extent by meditations on gratitude, future events, elevated emotions, and future intention. Finally, Gamma activity was increased to the greatest extent by meditations on gratitude, energy, and future intention.
These results suggest that different conscious content during meditation is reflected in differences in the activity of the brain in novice meditators. These understandings may be useful in identifying conscious content in real time during meditation. But these results need to be replicated in experienced meditators.
So, meditation on different states of consciousness produces different brain activity.
“mindfulness . . . has come to describe a meditation-based practice whose aim is to increase one’s sense of being in the present, but it has also been used to describe a nonmeditative state in which subjects set aside their mental distractions to pay greater attention to the here and now.” – Alvin Powell
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are also available on Google+ https://plus.google.com/106784388191201299496/posts and on Twitter @MindfulResearch
Study Summary
Stapleton, P., Dispenza, J., McGill, S., Sabot, D., Peach, M., & Raynor, D. (2020). Large effects of brief meditation intervention on EEG spectra in meditation novices. IBRO reports, 9, 290–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibror.2020.10.006
Abstract
This study investigated the impact of a brief meditation workshop on a sample of 223 novice meditators. Participants attended a three-day workshop comprising daily guided seated meditation sessions using music without vocals that focused on various emotional states and intentions (open focus). Based on the theory of integrative consciousness, it was hypothesized that altered states of consciousness would be experienced by participants during the meditation intervention as assessed using electroencephalogram (EEG). Brainwave power bands patterns were measured throughout the meditation training workshop, producing a total of 5616 EEG scans. Changes in conscious states were analysed using pre-meditation and post-meditation session measures of delta through to gamma oscillations. Results suggested the meditation intervention had large varying effects on EEG spectra (up to 50 % increase and 24 % decrease), and the speed of change from pre-meditation to post-meditation state of the EEG co-spectra was significant (with 0.76 probability of entering end-meditation state within the first minute). There was a main 5 % decrease in delta power (95 % HDI = [−0.07, −0.03]); a global increase in theta power of 29 % (95 % HDI = [0.27, 0.33]); a global increase of 16 % (95 % HDI = [0.13, 0.19]) in alpha power; a main effect of condition, with global beta power increasing by 17 % (95 % HDI = [0.15, 0.19]); and an 11 % increase (95 % HDI = [0.08, 0.14]) in gamma power from pre-meditation to end-meditation. Findings provided preliminary support for brief meditation in altering states of consciousness in novice meditators. Future clinical examination of meditation was recommended as an intervention for mental health conditions particularly associated with hippocampal impairments.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7649620/