Increase Telomere Length and Decrease Cellular Aging with Meditation
By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
“some forms of meditation may have salutary effects on telomere length by reducing cognitive stress and stress arousal and increasing positive states of mind and hormonal factors that may promote telomere maintenance.” – Elissa Epel
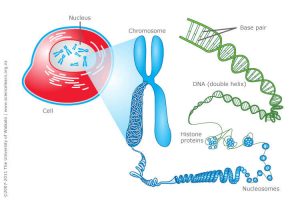
One of the most exciting findings in molecular biology in recent years was the discovery of the telomere. This is a component of the DNA molecule that is attached to the ends of the strands. Recent genetic research has suggested that the telomere and its regulation is the biological mechanism that produces aging. It has been found that the genes, coded on the DNA molecule, govern cellular processes in our bodies. One of the most fundamental of these processes is cell replication. Cells are constantly turning over. Dying cells or damaged are replaced by new cells. The cells turn over at different rates but most cells in the body are lost and replaced between every few days to every few months. Needless to say, we’re constantly renewing ourselves.
As we age the tail of the DNA molecule called the telomere shortens. When it gets very short cells have a more and more difficult time reproducing and become more likely to produce defective cells. On a cellular basis, this is what produces aging. As we get older the new cells produced are more and more likely to be defective. The shortening of the telomere occurs each time the cell is replaced. So, slowly as we age it gets shorter and shorter. This has been called a “mitotic clock.” This is normal. But telomere shortening can also be produced by oxidative stress, which can be produced by psychological and physiological stress. This is mediated by stress hormones and the inflammatory response. So, chronic stress can accelerate the aging process. In other words, when we’re chronically stressed, we get older faster.
Fortunately, there is a mechanism to protect the telomere. There is an enzyme in the body called telomerase that helps to prevent shortening of the telomere. It also promotes cell survival and enhances stress-resistance. Research suggests that processes that increase telomerase activity tend to slow the aging process by protecting the telomere. One activity that seems to increase telomerase activity and protect telomere length is mindfulness practice. Hence, engaging in mindfulness practices may protect the telomere and thereby slow the aging process. There is accumulating evidence, so it makes sense to stop and summarize what has been learned.
In today’s Research News article “Meditation and telomere length: a meta-analysis.” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://doi.org/10.1080/08870446.2019.1707827 ), Schutte and colleagues review, summarize, and perform a meta-analysis on the effects of meditation practice on cellular aging as reflected in telomere lengths. They identified 12 controlled published research studies.
They found that the published research demonstrated that meditation practices produce longer telomere lengths. The effect sizes were moderate and indicated that the meditation practitioners had telomeres about a half of a standard deviation longer then controls. They also report that the greater the number of hours of meditation practice the longer the telomeres, but this relationship was not significant in studies where there was a random assignment of participants to groups.
These are exciting findings that suggest that meditation practice can lead to greater telomere length. This in turn suggests that meditation would improve health and longevity. It is suspected that meditation has these benefits as the result of the ability of meditation practice to reduce the psychological and physiological responses to stress, where stress is known to have a shortening effect on the telomeres. Regardless of the mechanism, the accumulating research suggests that meditation can reduce cellular aging and thereby improve health and longevity.
Increase telomere length and decrease cellular aging with meditation.
“meditation and the like, which people can use to reduce stress and increase wellbeing, would be having their salutary and well-documented useful effects in part through telomeres.” – Elizabeth Blackburn
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are also available on Google+ https://plus.google.com/106784388191201299496/posts and on Twitter @MindfulResearch
Study Summary
Nicola S. Schutte, John M. Malouff & Shian-Ling Keng (2020): Meditation and telomere length: a meta-analysis, Psychology & Health, DOI: 10.1080/08870446.2019.1707827
ABSTRACT Objective: Telomeres are the caps at the end of chromosomes. Short telomeres are a biomarker for worsening health and early death. Design: The present study consolidated research on meditation and telomere length through a meta-analysis of results of studies examining the effect of meditation on telomere length by comparing the telomere length of meditating participants with participants in control conditions. Results: A search of the literature identified 11 studies reporting 12 comparisons of meditating individuals with individuals in control conditions. An overall significant weighted effect size of g ¼.40 indicated that the individuals in meditation conditions had longer telomeres. When an outlier effect size was trimmed from the analysis, the effect size was smaller, g ¼.16. Across studies, a greater number of hours of meditation among participants in meditation conditions was associated with larger effect sizes. Conclusion: These findings provide tentative support for the hypothesis that participants in meditation conditions have longer telomeres than participants in comparison conditions, and that a greater number of hours of meditation is associated with a greater impact on telomere biology. The results of the meta-analysis have potential clinical significance in that they suggest that meditation-based interventions may prevent telomere attrition or increase telomere length.
https://doi.org/10.1080/08870446.2019.1707827