Improve Knee and Hip Osteoarthritis with Exercise and Mind-Body Practices
By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
“studies suggest that specific mind-body therapies may help reduce pain and improve physical function in persons with osteoarthritis of the knee.” – Terry Selfe
Osteoarthritis is a chronic degenerative joint disease that is the most common form of arthritis. It produces pain, swelling, and stiffness of the joints. It is the leading cause of disability in the U.S., with about 43% of arthritis sufferers limited in mobility and about a third having limitations that affect their ability to perform their work. Knee osteoarthritis effects 5% of adults over 25 years of age and 12% of those over 65. Hip osteoarthritis effects 9% of adults. It is painful and disabling. Its causes are varied including, hereditary, injury including sports injuries, repetitive stress injuries, infection, or from being overweight.
There are no cures for knee or hip osteoarthritis. Treatments are primarily symptomatic, including weight loss, exercise, braces, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, arthroscopic knee surgery, or even knee or hip replacement. Gentle movements of the joints with exercise and physical therapy appear to be helpful in the treatment of knee or hip osteoarthritis. This suggests that alternative and mind-body practices that involve gentle knee movements may be useful in for treatment. Indeed, yoga practice has been shown to be effective in treating arthritis and Tai Chi and Qigong have also been shown to reduce the physical symptoms of knee osteoarthritis. So, it would seem reasonable to summarize the research into the effectiveness of mind-body practices relative to other exercises in treating knee or hip osteoarthritis.
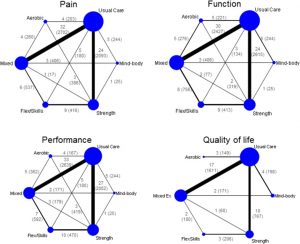
In today’s Research News article “Relative Efficacy of Different Exercises for Pain, Function, Performance and Quality of Life in Knee and Hip Osteoarthritis: Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis.” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6459784/), Goh and colleagues review, summarize, and perform a meta-analysis of the published research studies of the effectiveness of mind-body practices and exercise on knee or hip osteoarthritis. They found 103 controlled trials including a total of 9134 participants. Exercises were separated in strengthening, aerobic, and flexibility exercises and movements combined with mindfulness (e.g. yoga, Tai Chi, Qigong); mind-body practices. Most studies (76) compared these practices versus usual medical care.
They report that the published research studies found that in comparison to usual care, all exercises produced significant benefits including reduced pain, improved movement performance, self-reported motor abilities, and quality of life. These benefits were greater for knee osteoarthritis than for hip osteoarthritis. Of the various exercises they found that in general aerobic exercise produced the greatest benefits for pain and movement performance, while mind-body practices had equivalent benefit for pain and produced the greatest benefits for self-reported motor abilities.
These results confirm that exercise is good for patients with hip or knee osteoarthritis, improving movement and quality of life and reducing pain. It appears that aerobic exercises and mind-body exercises produce the greatest benefits. This suggests that these practices be recommended for patients with hip or knee osteoarthritis to reduce their difficulties with movement and reduce their suffering.
So, improve knee and hip osteoarthritis with exercise and mind-body practices.
“We don’t choose to have arthritis, but we can choose how to respond to and cope with it. By not allowing pain to define our lives, we can change how we view and relate to pain. That’s mindfulness – we are changing our feelings and thoughts around pain.” – Andrea Minick Rudolph
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are also available on Google+ https://plus.google.com/106784388191201299496/posts and on Twitter @MindfulResearch
Study Summary
Goh, S. L., Persson, M., Stocks, J., Hou, Y., Welton, N. J., Lin, J., … Zhang, W. (2019). Relative Efficacy of Different Exercises for Pain, Function, Performance and Quality of Life in Knee and Hip Osteoarthritis: Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Sports medicine (Auckland, N.Z.), 49(5), 743–761. doi:10.1007/s40279-019-01082-0
Abstract
Background
Guidelines recommend exercise as a core treatment for osteoarthritis (OA). However, it is unclear which type of exercise is most effective, leading to inconsistency between different recommendations.
Objectives
The aim of this systematic review and network meta-analysis was to investigate the relative efficacy of different exercises (aerobic, mind–body, strengthening, flexibility/skill, or mixed) for improving pain, function, performance and quality of life (QoL) for knee and hip OA at, or nearest to, 8 weeks.
Methods
We searched nine electronic databases up until December 2017 for randomised controlled trials that compared exercise with usual care or with another exercise type. Bayesian network meta-analysis was used to estimate the relative effect size (ES) and corresponding 95% credibility interval (CrI) (PROSPERO registration: CRD42016033865).
Findings
We identified and analysed 103 trials (9134 participants). Aerobic exercise was most beneficial for pain (ES 1.11; 95% CrI 0.69, 1.54) and performance (1.05; 0.63, 1.48). Mind–body exercise, which had pain benefit equivalent to that of aerobic exercise (1.11; 0.63, 1.59), was the best for function (0.81; 0.27, 1.36). Strengthening and flexibility/skill exercises improved multiple outcomes at a moderate level. Mixed exercise was the least effective for all outcomes and had significantly less pain relief than aerobic and mind–body exercises. The trend was significant for pain (p = 0.01), but not for function (p = 0.07), performance (p = 0.06) or QoL (p = 0.65).
Conclusion
The effect of exercise varies according to the type of exercise and target outcome. Aerobic or mind–body exercise may be the best for pain and function improvements. Strengthening and flexibility/skill exercises may be used for multiple outcomes. Mixed exercise is the least effective and the reason for this merits further investigation.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1007/s40279-019-01082-0) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Background
Guidelines recommend exercise as a core treatment for osteoarthritis (OA). However, it is unclear which type of exercise is most effective, leading to inconsistency between different recommendations.
Objectives
The aim of this systematic review and network meta-analysis was to investigate the relative efficacy of different exercises (aerobic, mind–body, strengthening, flexibility/skill, or mixed) for improving pain, function, performance and quality of life (QoL) for knee and hip OA at, or nearest to, 8 weeks.
Methods
We searched nine electronic databases up until December 2017 for randomised controlled trials that compared exercise with usual care or with another exercise type. Bayesian network meta-analysis was used to estimate the relative effect size (ES) and corresponding 95% credibility interval (CrI) (PROSPERO registration: CRD42016033865).
Findings
We identified and analysed 103 trials (9134 participants). Aerobic exercise was most beneficial for pain (ES 1.11; 95% CrI 0.69, 1.54) and performance (1.05; 0.63, 1.48). Mind–body exercise, which had pain benefit equivalent to that of aerobic exercise (1.11; 0.63, 1.59), was the best for function (0.81; 0.27, 1.36). Strengthening and flexibility/skill exercises improved multiple outcomes at a moderate level. Mixed exercise was the least effective for all outcomes and had significantly less pain relief than aerobic and mind–body exercises. The trend was significant for pain (p = 0.01), but not for function (p = 0.07), performance (p = 0.06) or QoL (p = 0.65).
Conclusion
The effect of exercise varies according to the type of exercise and target outcome. Aerobic or mind–body exercise may be the best for pain and function improvements. Strengthening and flexibility/skill exercises may be used for multiple outcomes. Mixed exercise is the least effective and the reason for this merits further investigation.
Key Points
| The effect of exercise in knee and hip osteoarthritis depends on type of exercise and outcome of interest. |
| Aerobic and mind–body exercises appear to be the two most effective exercise therapies for pain and function, whereas strengthening and flexibility exercises appear to be good for moderate improvement of multiple outcomes. |
| Mixed exercise is the least effective exercise. However, it may be used for patients who do not respond to other types of exercise therapy because it is still better than no exercise control for all four patient-centred outcomes. |
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6459784/