Increase Self-Compassion and Decrease Mind Wandering in Depression with Mindfulness
By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
“MBCT program is a group intervention that allows participants to become aware of how conditioned patterns of mind and mood can trigger depression relapse and sustain current symptoms of depression. Through the practice of mindful awareness, they develop the capacity to mindfully disengage from distressing moods and negative thoughts.” – Center for Mindfulness in Medicine
Clinically diagnosed depression is the most common mental illness, affecting over 6% of the population. But, of patients treated initially with drugs only about a third attained remission of the depression. After repeated and varied treatments including drugs, therapy, exercise etc. only about two thirds of patients attained remission. But drugs often have troubling side effects and can lose effectiveness over time.
Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) is an alternative treatment to drugs that was specifically developed to treat depression. MBCT involves mindfulness training, containing sitting, walking and body scan meditations, and cognitive therapy that attempts to teach patients to distinguish between thoughts, emotions, physical sensations, and behaviors, and to recognize irrational thinking styles and how they affect behavior. MBCT has been found to be effective in treating depression. The exact mechanisms by which MBCT improves depression need exploration.
In today’s Research News article “Compassionate Hearts Protect Against Wandering Minds: Self-compassion Moderates the Effect of Mind-Wandering on Depression.” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6426326/), Greenberg and colleagues recruited depressed adults and randomly assigned them to receive either 8 weekly 2-hour sessions of Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) or to a wait list control condition. MBCT participants were also asked to practice at home. All participants continued to receive their usual treatments. They were measured before and after treatment for depression, self-compassion, and mind wandering.
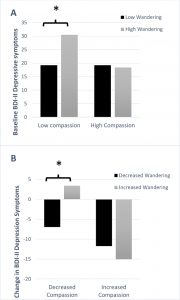
They found that prior to treatment the higher the levels of depression, the higher the levels of mind wandering and the lower the levels of self-compassion and that the higher the levels of self-compassion the lower the levels of mind wandering. They also found that participants who were low in mind wandering were significantly lower in depression, but only for participants who were also low in self-compassion. For those high in self-compassion there was no relationship between mind wandering and depression. Only those participants who were both low in self-compassion and high in mind wandering were depression scores high.
Compared to baseline and the wait-list controls, participants who received Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) had significantly greater reductions in depression and mind wandering and increases in self-compassion. They also found that the higher the levels of self-compassion at the beginning of training the larger the improvement in depression produced by MBCT. The improvements in depression were also associated with improvements in mind wandering.
The study reveals that self-compassion moderates the relationship of mind wandering with depression such that mind wandering is only associated with depression when self-compassion is low. In other words, when a participant has low levels of compassion for themselves they are vulnerable to the ability of a wandering mind to make depression worse. Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) was shown to improve depression, mind wandering, and self-compassion and the degree of impact of MBCT on depression was dependent on the levels of self-compassion, with high self-compassion associated with greater improvement.
So, self-compassion appears to be a critical variable in the relationship of mind wandering with depression and the effectiveness of MBCT on depression. This further suggests that training in self-compassion may be able to help reduce depression and improve the impact of mindfulness-based treatments on depression.
So, increase self-compassion and decrease mind wandering in depression with mindfulness.
“ When you’re struggling with depression, the last thing you want to do is be self-compassionate. But this is precisely what can help.” – Margarita Tartakovsky
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are also available on Google+ https://plus.google.com/106784388191201299496/posts and on Twitter @MindfulResearch
Study Summary
Greenberg, J., Datta, T., Shapero, B. G., Sevinc, G., Mischoulon, D., & Lazar, S. W. (2018). Compassionate Hearts Protect Against Wandering Minds: Self-compassion Moderates the Effect of Mind-Wandering on Depression. Spirituality in clinical practice (Washington, D.C.), 5(3), 155–169. doi:10.1037/scp0000168
Abstract
Depression is associated with high levels of mind-wandering and low levels of self-compassion. However, little is known about whether and how these two factors interact with one another to influence depressive symptoms. The current study examined the interaction between mind-wandering, self-compassion and depressive symptoms in a depressed sample and tested the effects of an eight-week Mindfulness Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) program on these constructs. At baseline, mind-wandering was associated with higher depressive symptoms only among individuals with low self-compassion. Self-compassion additionally predicted depressive improvement. As expected, MBCT increased self-compassion and reduced mind-wandering compared to a treatment-as-usual control group. Overall, longitudinal changes in self-compassion produced a moderation effect similar to the one at baseline so that increases in mind-wandering were associated with increases in depressive symptoms only among those who decreased in self-compassion. Results provide the first evidence that self-compassion can protect against the deleterious effects of mind-wandering among depressed participants, both at baseline and longitudinally. Findings also suggest that self-compassion is an effective predictor of depressive improvement. Finally, MBCT is effective not only at reducing depressive symptoms, but also at targeting protective and risk factors associated with depression.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6426326/