Reduce Anxiety and Depression in Patients with Mental and Physical Illness with Mindfulness
By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
“When you become aware of the present moment, you gain access to resources you may not have had before. You may not be able to change a situation, but you can mindfully change your response to it. You can choose a more constructive and productive way of dealing with stress rather than a counterproductive or even destructive way of dealing with it.” – Mindful
There are vast numbers of people worldwide who suffer with mental or physical illnesses. These illnesses often include or are accompanied by anxiety and depression which exacerbate the suffering. Mindfulness practices have been found to be helpful with coping with these illnesses and in many cases reducing the symptoms of the diseases. In addition, mindfulness practices have been found to relieve anxiety and depression. The mindfulness practices include mindfulness training, meditation, body scan, yoga, and a variety of mindful movement practices such as Tai Chi, Qigong, and Baduanjin. Baduanjin is a mind-body training that is very similar to Tai Chi and consists of 8 movements for limbs, body-trunk, and eye movements.
In today’s Research News article “Mindfulness-Based Baduanjin Exercise for Depression and Anxiety in People with Physical or Mental Illnesses: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5858390/ ), Zou and colleagues review, summarize and perform a meta-analysis of the effectiveness of Baduanjin practice for the relief of the anxiety and depression that often accompany mental and physical illnesses. They discovered 26 published randomized controlled studies.
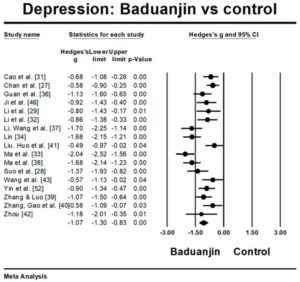
They found that the published studies showed large significant improvements in both anxiety and depression produced by Baduanjin practice; the amount of practice appeared to matter. The greater the number of hours of practice the lower the levels of anxiety and the greater the number of Baduanjin practice sessions the lower the levels of depression. Hence Baduanjin practice appears to significantly improve the psychological health of patients with mental and/or physical ailments in a dose response manner.
Baduanjin practice, like all mindful movement practices, is gentle and safe, having no appreciable side effects, it is appropriate for all ages including the elderly and for individuals with illnesses that limit their activities or range of motion, is inexpensive to administer, can be performed in groups or alone, at home or in a facility or even public park, and can be quickly learned. In addition, it can be practiced in social groups without professional supervision. This can make it fun, improving the likelihood of long-term engagement in the practice. So, Baduanjin practice would appear to be an almost ideal, safe and effective treatment for the anxiety and depression that often accompany other mental and physical illness.
So, reduce anxiety and depression in patients with mental and physical illness with mindfulness.
“Mindfulness keeps us focused on the present, and helps us meet challenges head on while we appreciate all our senses absorb. On the contrary, focus on the future contributes to anxiety, while perseveration on the past feeds depression. Far too often when we look to the future, we ask ourselves, “What if,” and the answer we give ourselves is often a prediction of a negative result.” – Vincent Fitzgerald
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are also available on Google+ https://plus.google.com/106784388191201299496/posts and on Twitter @MindfulResearch
Study Summary
Zou, L., Yeung, A., Quan, X., Hui, S. S.-C., Hu, X., Chan, J. S. M., … Wang, H. (2018). Mindfulness-Based Baduanjin Exercise for Depression and Anxiety in People with Physical or Mental Illnesses: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(2), 321. http://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15020321
Abstract
Objectives: we used a quantitative method to systematically synthesize the emerging literature and critically evaluate the effects of Baduanjin on depression and anxiety in people with physical or mental illnesses. Additionally, we determined if the number of total Baduanjin training sessions is associated with decreased anxiety and depression levels. Methods: both English and Chinese databases were searched for potential studies published between January 1982 and October 2017. The eligible randomized controlled trials were considered for meta-analysis. Effect size (Hedge’s g) was computed for the pooled effects while the random-effect model was set. For moderator analysis; Subgroup meta-analysis for categorical variables and meta-regression for continuous variables were performed. Results: the aggregated result has shown a significant benefit in favour of Baduanjin on anxiety (Hedge’s g = −0.99; CI −1.63 to −0.74) and depression (Hedge’s g = −1.07; CI −1.3 to −0.83). For continuous potential moderators; meta-regression indicated a significant effect for total hours in Baduanjin practice (β = −0.0053; 95% CI −0.009 to −0.0014; p = 0.008). With regard to depression; meta-regression indicated a significant effect for total sessions of Baduanjin practice (β = −0.0023; 95% CI −0.006 to −0.0004; p = 0.028). Conclusions: the encouraging findings indicate the efficacy of Baduanjin exercise in reducing depression and anxiety symptoms in people with physical or mental illnesses. However; the results should be interpreted with caution because of existing methodological limitations (e.g., high risk of bias; Baduanjin combined with other behavioral interventions; and heterogeneity of control groups).
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5858390/