By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
In today’s Research News article “Long-term effects of yoga-based practices on neural, cognitive, psychological, and physiological outcomes in adults: a scoping review and evidence map.” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11884082/ ) Campelo and colleagues review and summarize the effects of long-term yoga practice on the physiological and psychological states of yoga practitioners. They report that yoga practice produces long-term changes in brain systems underlying sensorimotor, interoceptive, emotion regulation, and executive functions and in the periphery increases in parasympathetic-driven autonomic, hormonal and immune responses. Yoga practice also reduces negative emotions, psychopathology, and emotional reactivity as well as improved memory and cognition.
Long-term yoga practice positively alters the physiological and psychological state of the practitioners.
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are also available on the Contemplative Studies Blog http://contemplative-studies.org
Study Summary
Campelo G, de Araújo JR, Aristizabal JP, de Souza W, de Castilho GM. Long-term effects of yoga-based practices on neural, cognitive, psychological, and physiological outcomes in adults: a scoping review and evidence map. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025 Mar 6;25(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s12906-025-04825-x. PMID: 40050913; PMCID: PMC11884082.
Abstract
Background
Compared with short-term practices, long-term yoga might promote differential qualitative and quantitative outcomes. Following JBI’s and PRISMA-ScR guidelines, this scoping review followed an apriori and systematic protocol to document the long-term effects of yoga on neural, cognitive, psychological, and physiological outcomes, provide evidence maps for each yoga component, and summarize results identifying knowledge gaps and promising directions.
Methods
Four databases (PubMed, Cochrane, LILACS, and PubPsych) were last searched in March 2023. Studies were included if they evaluated adults with > 1 year of practice, specified yoga-based practice(s) of interest, measured neural, cognitive, psychological, and/or physiological outcomes, were written in English, Spanish, or Portuguese, presented original data, and mentioned search terms in the title/abstract. Evidence maps for each yoga component followed a 4-level structure of outcome category, method, study design and literature size. Qualitative summaries followed the same structure, to facilitate information retrieval.
Results
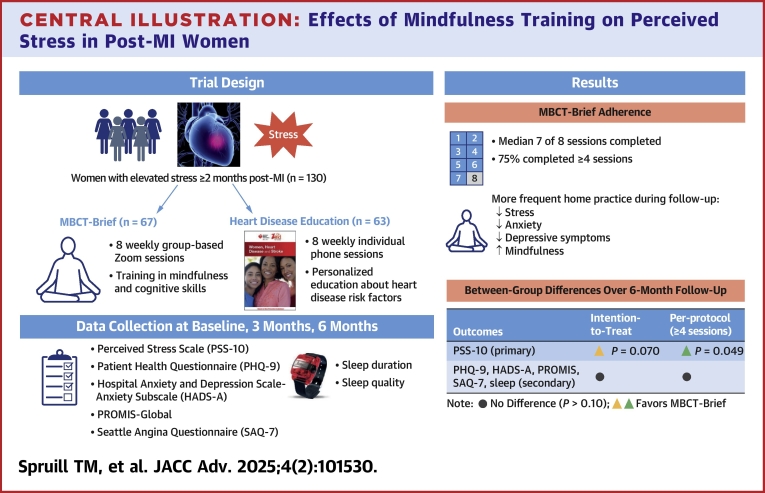
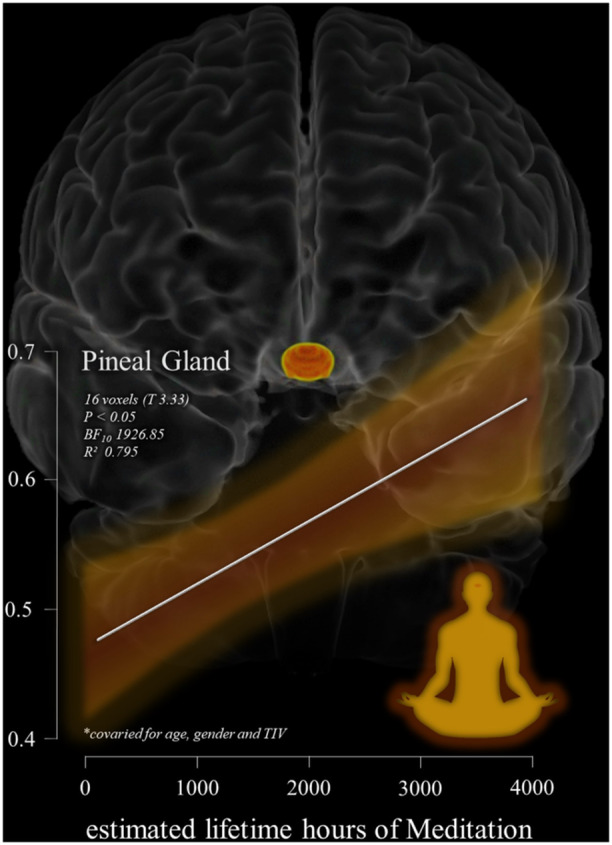
Out of 2270 screened studies, 65 were included (meditative studies = 36, predominantly postural studies = 25, breathing practice studies = 8). Physiologicaland neural outcomes were the most common, followed by psychological and cognitive outcomes. Although heterogeneous, neural results reveal structural and functional changes related to sensorimotor, interoceptive, emotion regulation, and executive functions. Physiologically, most studies have associated long-term practice with parasympathetic-driven autonomic, hormonal and immune responses, but some studies revealed sympathetic-driven or mixed responses, maybe due to the specific technique or individual differences. Psychological outcomes included lower levels of negative affect, psychopathological symptoms, and emotional reactivity. Cognitive measures have shown improved memory/cognition for older adults, but mixed or null effects for other constructs. Commonly, however, long-term practitioners demonstrated improved neural or physiological efficiency while performing cognitive tasks.
Conclusions
Future research should provide clear descriptions of the investigated yoga practice, employ more experimental paradigms, and refine statistical reports and models. We encourage researchers to work with specific overarching theoretical frameworks to refine research predictions, such as the neurovisceral integration model or predictive coding models; to consider motivational, cultural, and contextual factors that might influence long-term outcomes; and to develop systematic reviews and meta-analyses as next steps of evidence summary.
 By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.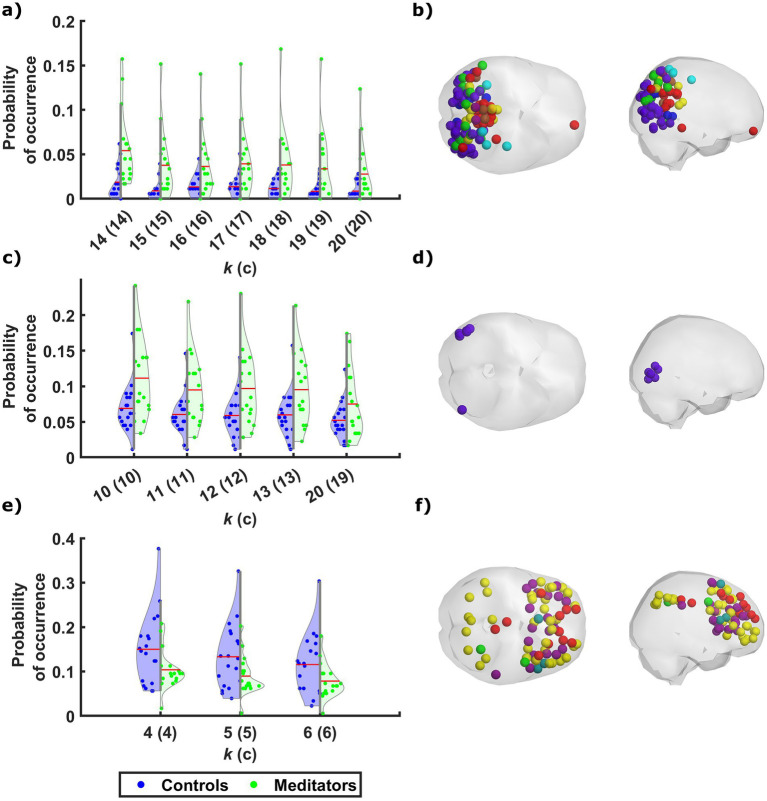

 By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.