By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
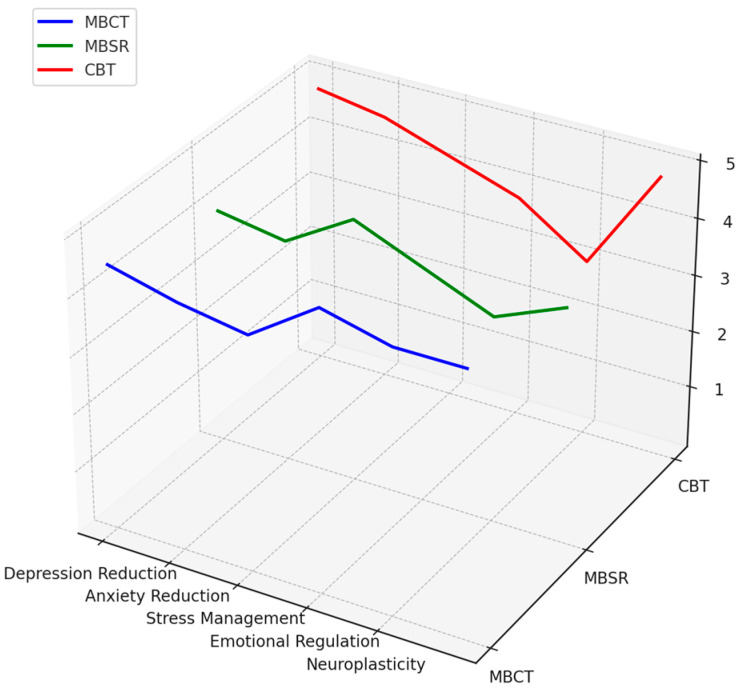
In today’s Research News article “Effectiveness of an age-modified mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT) in improving mental health in older people with depressive symptoms: a non-randomised controlled trial” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11863447/) Wang and colleagues studied the effectiveness of mindfulness teacher and social worker led Mindfulness Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) for the relief of depression and stress in adults over 60 years of age. They found that the training significantly decreased depression and perceived stress and increased mindful non-reactivity in the older adults.
Mindfulness Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) improves mental health in older adults.
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are also available on the Contemplative Studies Blog http://contemplative-studies.org
Study Summary
Wang YH, Wang YL, Leung DKY, Ng ZLY, Chan OLH, Wong SMY, Chan RCL, Liu T, Wong GHY, Lum TYS. Effectiveness of an age-modified mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT) in improving mental health in older people with depressive symptoms: a non-randomised controlled trial. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025 Feb 26;25(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s12906-025-04781-6. PMID: 40011881; PMCID: PMC11863447.
Abstract
Background
Emerging evidence has shown that mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT) is effective in improving depressive symptoms in the older population. However, the accessibility to MBCT is limited by the shortage of psychotherapists or mindfulness teachers. One potential solution is to involve social workers, who have the knowledge and skills to promote individual and community well-being in various settings, in delivering modified MBCT to enhance its accessibility and sustainability. This study examined the effectiveness of an eight-week age-modified MBCT led by different mental health professionals (mindfulness teacher only vs. mindfulness teacher and social worker) in improving mental health outcomes as compared with a control group.
Methods
Older adults (N = 112) were recruited through five community-based centres for older adults and mental wellness in Hong Kong. Participants were allocated to one of three groups: (1) mindfulness teacher-led modified MBCT, (2) social worker/teacher co-led modified MBCT (50% led by social workers and 50% led by mindfulness teacher), or (3) control (care as usual). The age-modified MBCT consisted of eight weekly sessions, with age-related modifications including more sitting meditation, shortened duration of each session, and the removal of the retreat. Outcome variables (i.e., depressive symptoms, anxiety symptoms, perceived stress, and mindfulness) were assessed at baseline (T0), after the intervention (T1), and four weeks after the intervention (T2), through self-reported questionnaires. Linear mixed models were performed while controlling for demographic variables to examine changes in outcome variables between the groups.
Results
Participants from the age-modified MBCT intervention groups (teacher-led and social worker/teacher co-led) showed significantly greater reductions in depressive symptoms and stress, as well as greater increase in mindful non-reactivity, compared to the control group post-intervention. No significant interaction effect of time and group was found for anxiety and both overall mindfulness and its other facets. The improvements in mental health and mindfulness outcomes post-intervention were not significantly different between the teacher-led and social worker/teacher co-led MCBT groups.
Discussion
Age-modified MBCT is beneficial in managing depressive and stress symptoms and in improving mindful non-reactivity among older adults at risk for depression. The findings support the feasibility and effectiveness of partial task-shifting in the delivery of MBCT to trained social workers. Future studies may explore the possibility for social workers in leading MBCTs independently to further improve its scalability and service accessibility for older adults in the community.