By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
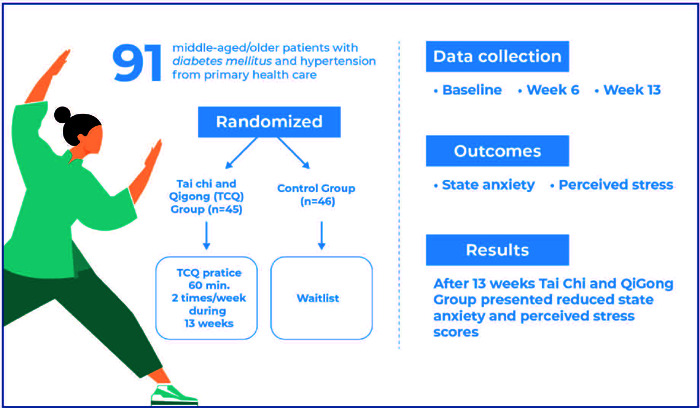
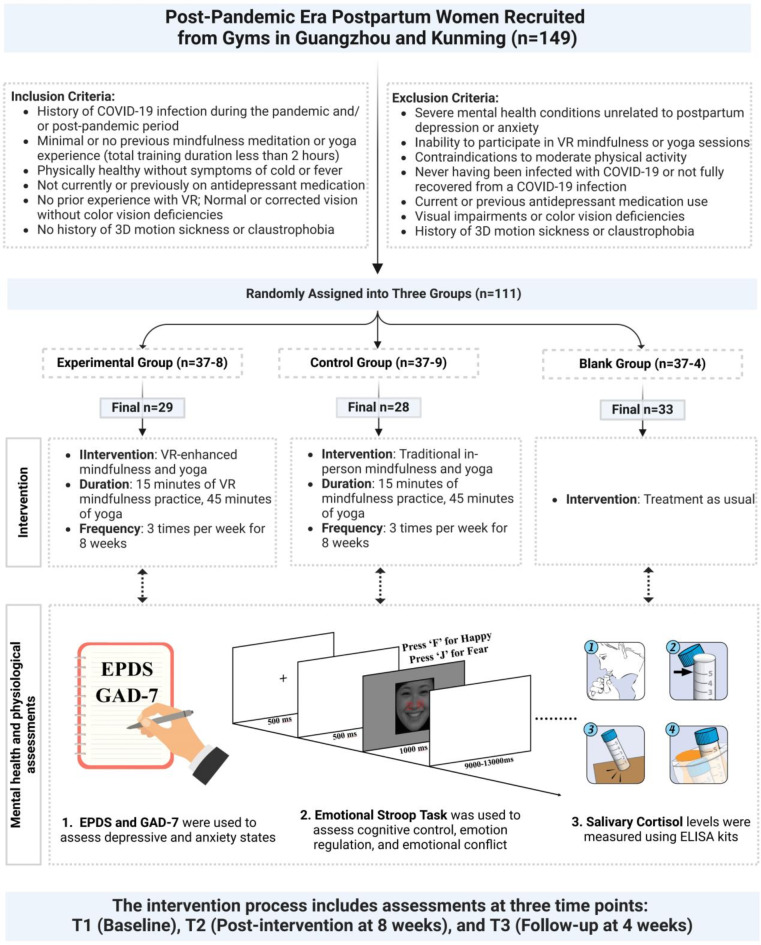
In today’s Research News article “Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy in Clinical Practice: A Systematic Review of Neurocognitive Outcomes and Applications for Mental Health and Well-Being” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11900371/) Gkintoni and colleagues Review and summarize the published research studies of the effectiveness of Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) for the treatment of psychological issues. They report that MBCT has been shown to be effective in the treatment of depression, anxiety, and stress and to improve cognitive function and the regulation of emotions.
Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy is and effective therapy for a variety of psychological issues.
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are also available on the Contemplative Studies Blog http://contemplative-studies.org
Study Summary
Gkintoni E, Vassilopoulos SP, Nikolaou G. Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy in Clinical Practice: A Systematic Review of Neurocognitive Outcomes and Applications for Mental Health and Well-Being. J Clin Med. 2025 Mar 3;14(5):1703. doi: 10.3390/jcm14051703. PMID: 40095733; PMCID: PMC11900371.
Abstract
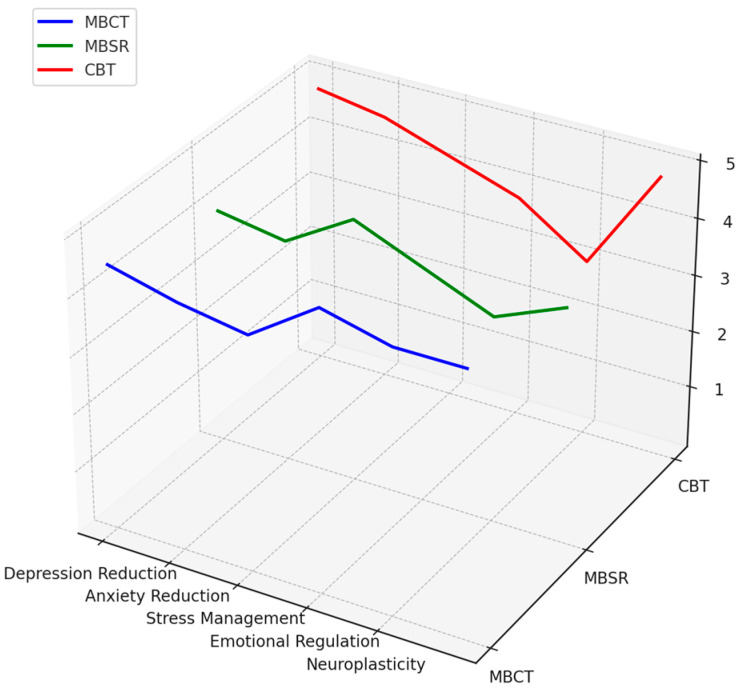
Background/Objectives: This systematic review outlines the neurocognitive outcomes and mechanisms of mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT) that influence subjective well-being. MBCT is a clinical intervention that integrates cognitive therapy with mindfulness practices to prevent depression relapses and improve mental health. Methods: The review focuses on the effects of MBCT on brain structure changes, cognitive processes, and emotional regulation, which are related to improvements in subjective well-being. A total of 87 studies were included in the review to assess the effectiveness of MBCT. Results: Evidence from the studies highlights the effectiveness of MBCT in reducing symptoms of depression, anxiety, and stress. MBCT was also shown to enhance cognitive functions and emotional regulation across diverse populations. These findings point to the potential for MBCT to induce neuroplastic changes in the brain and widen the applicability of the treatment for a variety of disorders, calling for further research into long-term benefits and underlying neurobiological mechanisms. Conclusions: The review emphasizes the potential of MBCT to bring about neuroplastic changes, calling for further research into its long-term benefits and the underlying neurobiological mechanisms. This study underlines the need to incorporate multidisciplinary measures by integrating psychology and neuroscience to comprehend comprehensively the effects of MBCT.