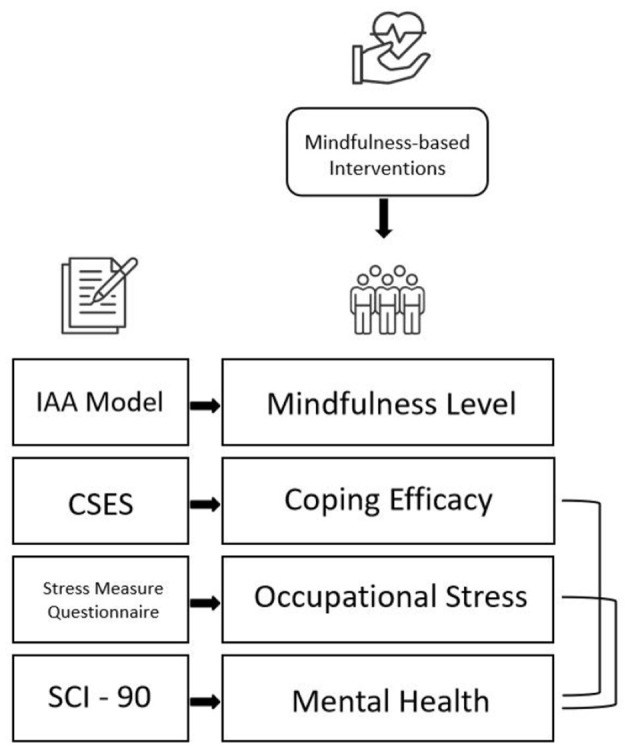
By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
In today’s Research News article “Behavioral interventions for migraine prevention: A systematic review and meta-analysis” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11951403/ ) Treadwell and colleagues review, summarize, and perform a meta-analysis of the published research on the effectiveness of mindfulness-based therapies for the treatment of migraine headaches. They report that the research indicates that mindfulness-based therapies are effective in reducing the frequency of migraine headaches and the disability produced by the headaches.
Treat migraines with mindfulness.
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are also available on the Contemplative Studies Blog http://contemplative-studies.org
Study Summary
Treadwell JR, Tsou AY, Rouse B, Ivlev I, Fricke J, Buse DC, Powers SW, Minen M, Szperka CL, Mull NK. Behavioral interventions for migraine prevention: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Headache. 2025 Apr;65(4):668-694. doi: 10.1111/head.14914. Epub 2025 Feb 19. PMID: 39968795; PMCID: PMC11951403.
Abstract
Objectives/Background
This study was undertaken to synthesize evidence on the benefits and harms of behavioral interventions for migraine prevention in children and adults. The efficacy and safety of behavioral interventions for migraine prevention have not been tested in recent systematic reviews.
Methods
An expert panel including clinical psychologists, neurologists, primary care physicians, researchers, funders, individuals with migraine, and their caregivers informed the scope and methods. We searched MEDLINE, Embase, PsycINFO, PubMed, the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, clinicaltrials.gov, and gray literature for English‐language randomized trials (January 1, 1975 to August 24, 2023) of behavioral interventions for preventing migraine attacks. Primary outcomes were migraine/headache frequency, migraine disability, and migraine‐related quality of life. One reviewer extracted data and rated the risk of bias, and a second verified data for completeness and accuracy. Data were synthesized with meta‐analysis when deemed appropriate, and we rated the strength of evidence (SOE) using established methods.
Results
For adults, we included 50 trials (77 publications, N = 6024 adults). Most interventions were multicomponent (e.g., cognitive behavioral therapy [CBT], biofeedback, relaxation training, mindfulness‐based therapies, and/or education). Most trials were at high risk of bias, primarily due to possible measurement bias and incomplete data. For adults, we found that any of three components (CBT, relaxation training, mindfulness‐based therapies) may reduce migraine/headache attack frequency (SOE: low). Education alone that targets behavior may improve migraine‐related disability (SOE: low). For three other interventions (biofeedback, acceptance and commitment therapy, and hypnotherapy), evidence was insufficient to permit conclusions. We also found that mindfulness‐based therapies may reduce migraine disability more than education, and relaxation + education may improve migraine‐related quality of life more than propranolol (SOE: low). For children/adolescents, we included 13 trials (16 publications, N = 1444 children), but the evidence was only sufficient to conclude that CBT + biofeedback + relaxation training may reduce migraine attack frequency and disability more than education alone (SOE: low).
Conclusion
Results suggest that for adults, CBT, relaxation training, and mindfulness‐based therapies may each reduce the frequency of migraine/headache attacks, and education alone may reduce disability. For children/adolescents, CBT + biofeedback + relaxation training may reduce migraine attack frequency and disability more than education alone. Evidence consisted primarily of underpowered trials of multicomponent interventions compared with various types of control groups. Limitations include semantic inconsistencies in the literature since 1975, differential usage of treatment components, expectation effects for subjectively reported outcomes, incomplete data, and unclear dosing effects. Future research should enroll children and adolescents, standardize intervention components when possible to improve reproducibility, consider smart study designs and personalized therapies based on individual characteristics, use comparison groups that control for expectation, which is a known challenge in behavioral trials, enroll and retain larger samples, study emerging digital and telehealth modes of care delivery, improve the completeness of data collection, and establish or update clinical trial conduct and reporting guidelines that are appropriate for the conduct of studies of behavioral therapies.