Different Meditation Types Alter Brain Connectivity Patters Differently Over the Long Term
By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
“[Meditation], regardless of each individual’s chosen object of attention, increases functional connectivity within attentional networks as well as increases connectivity across distributed brain regions serving attention, self-referential, and visual processes.” – Zongpai Zhang
There has accumulated a large amount of research demonstrating that meditation practice has significant benefits for psychological, physical, and spiritual wellbeing. One way that meditation practices may produce these benefits is by altering the brain. The nervous system is a dynamic entity, constantly changing and adapting to the environment. It will change size, activity, and connectivity in response to experience. These changes in the brain are called neuroplasticity. Over the last decade neuroscience has been studying the effects of contemplative practices on the brain and has identified neuroplastic changes in widespread areas. In other words, meditation practice appears to mold and change the brain, producing psychological, physical, and spiritual benefits.
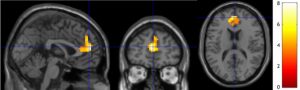
In today’s Research News article “Neuroplasticity within and between Functional Brain Networks in Mental Training Based on Long-Term Meditation.” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8393942/ ) Guidotti and colleagues recruited Buddhist monks highly experienced with both focused and open monitoring meditation (average of 16.4 years of practice with an average of 1200 hours of practice per year). They underwent functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) brain scans during 6-minute meditations with focused and with open monitoring techniques.
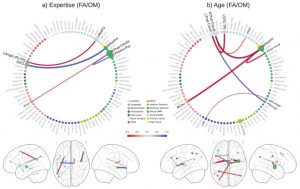
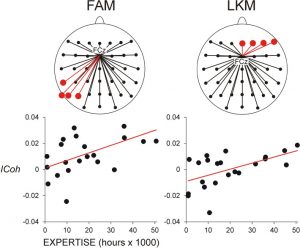
They found that connectivity patterns were associated with the age of the participants during both meditation techniques. On the other hand, connectivity patterns were associated with years of meditation experience differently during focused versus open monitoring meditation. During both meditation types the functional connectivity within the Salience Network of the brain was reduced. During focused meditation there was increased connectivity within the Visual Network. During open monitoring meditation there was increase connectivity within the Executive Network and between the Executive and Language Networks. During open monitoring meditation there was also increase connectivity with Sensorimotor Network and its connections with the Default Mode Network.
These results are complicated and involve only experienced meditators. So, it is unknown whether the findings apply to novice or less experienced meditators and it cannot be determined what the differences might be in the brains of these highly experience meditators compared to non-meditators. But the results suggest that during focused and open monitoring meditation types have the same relationships with age related connectivity patterns in the brain while they have different associations with connectivity patterns in association with experience. This suggests that the two meditation types produce different neuroplastic changes in the brain as experience accumulates.
So, different meditation types alter brain connectivity patters differently over the long term.
“people who meditate may actually have quicker brains than the rest of us. . . meditation can improve your brain’s ability to quickly switch between two main states of consciousness.” – Katie Spalding
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are also available on Google+ https://plus.google.com/106784388191201299496/posts and on Twitter @MindfulResearch
Study Summary
Guidotti, R., Del Gratta, C., Perrucci, M. G., Romani, G. L., & Raffone, A. (2021). Neuroplasticity within and between Functional Brain Networks in Mental Training Based on Long-Term Meditation. Brain sciences, 11(8), 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11081086
Abstract
(1) The effects of intensive mental training based on meditation on the functional and structural organization of the human brain have been addressed by several neuroscientific studies. However, how large-scale connectivity patterns are affected by long-term practice of the main forms of meditation, Focused Attention (FA) and Open Monitoring (OM), as well as by aging, has not yet been elucidated. (2) Using functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) and multivariate pattern analysis, we investigated the impact of meditation expertise and age on functional connectivity patterns in large-scale brain networks during different meditation styles in long-term meditators. (3) The results show that fMRI connectivity patterns in multiple key brain networks can differentially predict the meditation expertise and age of long-term meditators. Expertise-predictive patterns are differently affected by FA and OM, while age-predictive patterns are not influenced by the meditation form. The FA meditation connectivity pattern modulated by expertise included nodes and connections implicated in focusing, sustaining and monitoring attention, while OM patterns included nodes associated with cognitive control and emotion regulation. (4) The study highlights a long-term effect of meditation practice on multivariate patterns of functional brain connectivity and suggests that meditation expertise is associated with specific neuroplastic changes in connectivity patterns within and between multiple brain networks.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8393942/