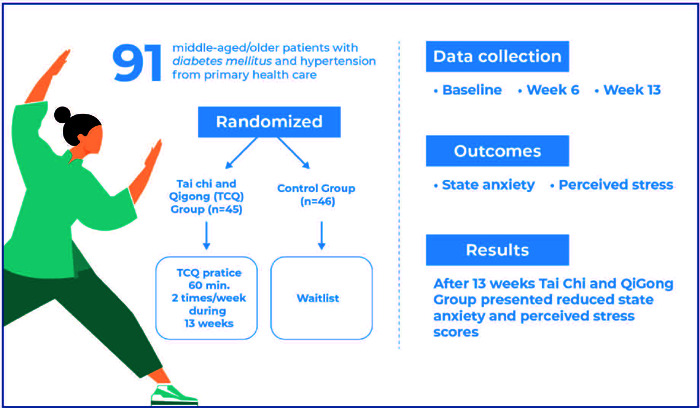
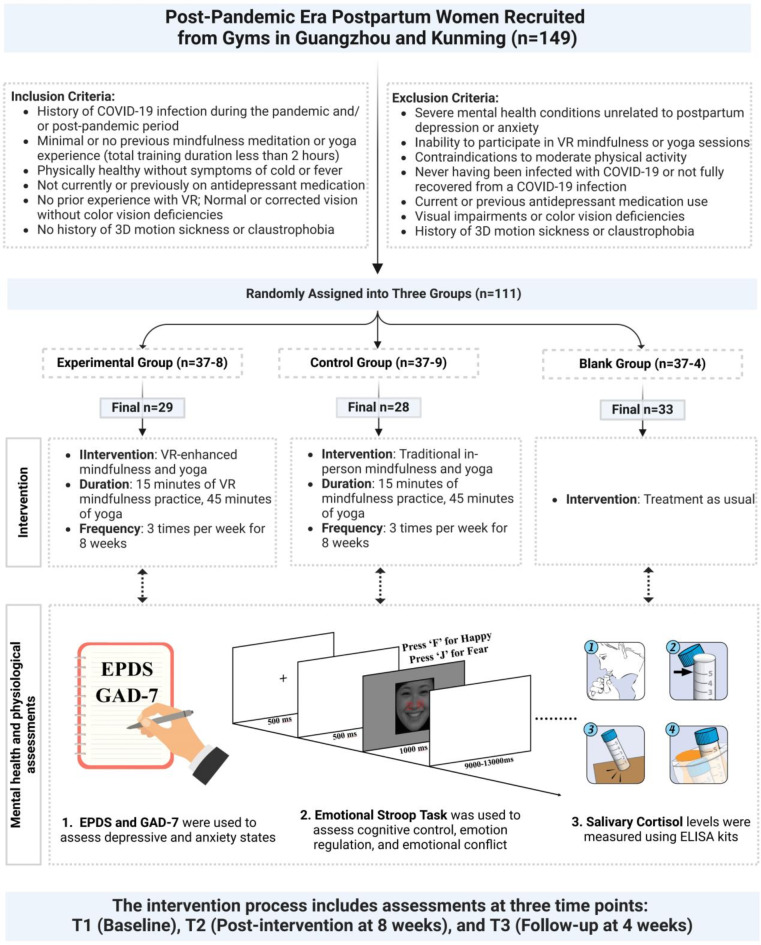
By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
In today’s Research News article “The Effect of Medication Adherence and Spirituality in Quality of Life of Patients with Rheumatic Diseases” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11855639/) Kavvadia and colleagues examined the relationships of spirituality with health and quality of life in patients with the Rheumatic Diseases of rheumatoid arthritis or lupus, They report that spirituality is significantly associated with the quality of life of these patients and their physical and psychological health.
Spirituality was associated with enhanced well-being and quality of life in patients with Rheumatic Diseases.
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are also available on the Contemplative Studies Blog http://contemplative-studies.org
Study Summary
Kavvadia M, Saridi M, Toska A, et al. The Effect of Medication Adherence and Spirituality in Quality of Life of Patients with Rheumatic Diseases. Healthcare (Basel). 2025;13(4):436. Published 2025 Feb 18. doi:10.3390/healthcare13040436
Abstract
Background: Spirituality is significantly associated with the quality of life of patients suffering from rheumatic diseases, helping them to cope with pain and improve emotional well-being. There is a gap in the literature regarding the relationship between spirituality, quality of life and treatment adherence in patients with rheumatic diseases, especially rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), as relevant studies, especially in the Greek population, are limited. Aims: The present study aimed to evaluate the effect of medication adherence and spirituality on the quality of life of patients with rheumatic diseases. Methods: This was a cross-sectional study conducted in adult patients with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus from the region of Crete. Data were collected via a self-administrated questionnaire consisting of four parts, including questions regarding demographic and clinical information; the WHOQoL-BREF, 3, FACIT-Sp-12, and SMAQ questionnaires were used. The level of statistical significance was set at α = 0.05 for all analyses. Results: The study sample consisted of 115 participants, with the majority being women (90%). The majority of the participants suffered from RA (62%), while 38% suffered from SLE. The mean age of the participants was 49.15 years (SD = 11.7), and 46% described their health as good. We found that the dimensions of spirituality are positively related to the dimensions of quality of life. The peace dimension has a strong correlation with psychological health (r = 0.679, p < 0.001) and overall quality of life (QOL Global, r = 0.671, p < 0.001). Meaning also shows a positive correlation with psychological health (r = 0.563, p < 0.001) and overall quality of life (r = 0.506, p < 0.001), whereas adherence to medication shows a low but positive correlation with overall spirituality (r = 0.192, p = 0.040). Conclusions: The findings support that spirituality can be a protective mechanism, improving the mental resilience and adaptability of patients. This study has the potential to contribute to the development of evidence-based guidelines for the integration of spiritual care into clinical practice, with the objective of enhancing the psychological well-being and overall quality of life of patients with rheumatic diseases.