Spirituality May Alter the Brain to Protect Against Major Depression
By John M. de Castro, Ph.D.
“spirituality or religion may protect against major depression by thickening the brain cortex and counteracting the cortical thinning that would normally occur with major depression.” – Lisa Miller
Spirituality is defined as “one’s personal affirmation of and relationship to a higher power or to the sacred. Spirituality has been promulgated as a solution to the challenges of life both in a transcendent sense and in a practical sense. There have been a number of studies of the influence of spirituality on the physical and psychological well-being of practitioners mostly showing positive benefits, with spirituality encouraging personal growth and mental health.
One way that spirituality can have its effects on the individual is by altering the brain. The nervous system is a dynamic entity, constantly changing and adapting to the environment. It will change size, activity, and connectivity in response to experience. These changes in the brain are called neuroplasticity. Over the last decade neuroscience has been studying the effects of contemplative practices on the brain and has identified neuroplastic changes in widespread area. and have found that meditation practice appears to mold and change the brain, producing psychological, physical, and spiritual benefits. So, religion and spirituality may be associated with changes in the nervous system associated with better mental health.
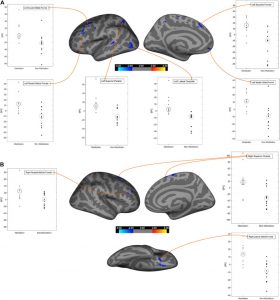
In today’s Research News article “Altruism and “love of neighbor” offer neuroanatomical protection against depression. Psychiatry research.” (See summary below or view the full text of the study at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8672211/ ) Miller and colleagues reanalyzed longitudinal data obtained from individuals at risk for major depression and matched normal participants. At 30 and 35 years of age the participants brains were scanned with Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and the participants completed measures of major depressive disorder, level of depression and spirituality including measures of altruism, love thy neighbor as self, interconnectedness, contemplative practice, and commitment to religion/spirituality.
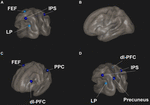
They found that the low risk of depression group had significantly greater cortical thickness in the Ventral Frontotemporal Network (VFTN), in comparison to the high-risk group. The VFTN had been previously shown to be associated with spiritual experience. They also found that in the at-risk for major depression group the greater the cortical thickness in the VFTN the lower levels of depression and the lower the risk of developing major depressive disorder. Across all participants, the higher the spirituality measures of altruism and love thy neighbor as self the greater the cortical thickness in the VFTN. In addition, in the high-risk group, the higher the levels of the spirituality measure of love thy neighbor as self the lower the levels of depression and the lower the risk of developing major depressive disorder.
The results demonstrate that the thickness of the Ventral Frontotemporal Network (VFTN) is associated with lower levels of depression and risk of major depressive disorder. In addition, thee results suggest that for people with a high risk of developing major depressive disorder spirituality particularly in the of altruism and love thy neighbor as self categories is associated with protection of the cortical areas from deterioration and this in turn is associated with lower depression and risk of major depressive disorder.
These results suggest that spirituality is associated protection from depression by protecting the brain particularly in people at high risk of developing major depressive disorder. These are correlative results, so it is not possible to determine causation. Future research needs to determine if promotion of spirituality, perhaps by training in contemplative practices, might produce neuroplastic changes in the brain and protect against the development of major depressive disorder.
So, spirituality may alter the brain to protect against major depression.
“there is neurobiological basis of spirituality and depression risk. It is unlikely to be harmful, and may very well help to steer the religious depressed patient to more spiritual contemplation, and the non-religious one to more meditation and reflection.” – Emily Deans
CMCS – Center for Mindfulness and Contemplative Studies
This and other Contemplative Studies posts are available on Twitter @MindfulResearch
Study Summary
Miller, L., Wickramaratne, P., Hao, X., McClintock, C. H., Pan, L., Svob, C., & Weissman, M. M. (2021). Altruism and “love of neighbor” offer neuroanatomical protection against depression. Psychiatry research. Neuroimaging, 315, 111326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pscychresns.2021.111326
Abstract
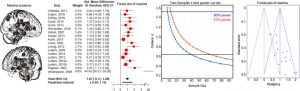
We prospectively investigate protective benefits against depression of cortical thickness across nine regions of a Ventral Frontotemporal Network (VFTN), previously associated with spiritual experience. Seventy-two participants at high and low risk for depression (Mean age 41 years; 22–63 years; 40 high risk, 32 low risk) were drawn from a three-generation, thirty-eight year study. FreeSurfer estimated cortical thickness over anatomical MRIs of the brain (Year 30) for each of the nine ROIs. Depression (MDD with SAD-L; symptoms with PHQ; Years 30 and 38) and spirituality (self-report on five phenotypes; Year 35), respectively, were associated with the weighted average of nine regions of interest. VFTN thickness was: 1) positively associated (p<0.01) with two of five spiritual phenotypes, altruism and love of neighbor, interconnectedness at a trend level, but neither commitment nor practice, 2) inversely associated with a diagnosis of MDD (SADS-L Year 30, for any MDD in the past ten years), and 3) prospectively neuroanatomically protective against depressive symptoms (PHQ-9 Year 38) for those at high familial risk.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8672211/